Netgear WPNT511 WPNT511 User Manual - Page 9
Introduction, About the NETGEAR RangeMax™ 240 Wireless Notebook Adapter WPNT511 - pcmcia wireless network adapter
 |
UPC - 606449044799
View all Netgear WPNT511 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
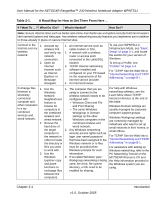
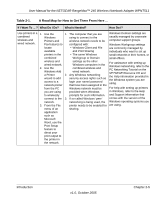
Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter introduces the features, package contents, and appearance of the NETGEAR RangeMax™ 240 Wireless Notebook Adapter WPNT511. About the NETGEAR RangeMax™ 240 Wireless Notebook Adapter WPNT511 The NETGEAR RangeMax™ 240 Wireless Notebook Adapter WPNT511 gives you ultimate mobility in your office or while you are traveling. It frees you from traditional Ethernet wiring and helps you create a wireless network for sharing your broadband cable or DSL Internet access among multiple PCs in and around your home. It is designed for notebook computers running Microsoft® Windows®. It is both 16-bit PCMCIA and 32-bit CardBus compatible and works in any available PCMCIA or CardBus slot. Its auto-sensing capability allows high packet transfer at up to 240 Mbps for maximum throughput or dynamic range shifting to lower speeds due to distance or operating limitations in an environment with a lot of electromagnetic interference. The WPNT511 Wireless Notebook Adapter provides reliable, standards-based 802.11b, 11 Mbps, and 802.11g 54 Mbps WLAN connectivity that is protected with industry-standard security. In addition, it offers the faster speeds of MIMO technology. It works with Windows 2000 SP4, and XP operating systems. Key Features The WPNT511 Wireless Notebook Adapter provides the following features: • Reliable IEEE 802.11g and b standards-based wireless technology. • Supports roaming between access points when configured in Infrastructure mode. • High-speed data transfer of 240 Mbps. Wireless nodes negotiate to operate in the optimal data transfer rate. In a noisy environment or when the distance between the wireless nodes is far, the wireless nodes automatically fall back to operate at lower transfer rates. Introduction v1.0, October 2005 Chapter 2-1