Yamaha DVR-S150 Owners Manual - Page 95
Video signal information, Track CD/Video CD, YPAO YAMAHA Parametric Room, Acoustic Optimizer
 |
View all Yamaha DVR-S150 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 95 highlights
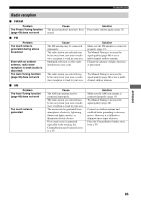
Glossary ■ Track (CD/Video CD) A CD or Video CD can be divided into a number of segments (tracks). Each division is called a title number. ■ YPAO (YAMAHA Parametric Room Acoustic Optimizer) YPAO is an original YAMAHA system that configures speaker settings such as speaker balance (volume level of each speaker), delay time of each channel, and crossover/ high cut frequency for the subwoofer automatically. YPAO uses the supplied optimizer microphone to collect and analyze sounds output from the speakers in the actual listening environment. Video signal information ■ Component video signal With the component video signal system, the video signal is separated into the Y signal for the luminance and the PB and PR signals for the chrominance. Color can be reproduced more faithfully with this system because each of these signals is independent. The component signal is also called the "color difference signal" because the luminance signal is subtracted from the color signal. ■ Decoder A device that converts encoded data on DVD and other media back to its original audio or video signal. ■ Film and video data In general, DVD media can be classified into the 2 types below. • Film Data Video recorded at 24 frames/second. (The film used for shooting movies is recorded at 24 frames/second.) Recently 30 frames/second progressive video has made its debut. • Video Data Video recorded at 30 frames/second. CinemaStation will automatically recognize whether the source recorded on DVD is film or video, then select the best method to convert it into progressive output. ■ Interlace and progressive outputs Up to now the standard video signal has been NTSC with 525i (i: interlaced) scan lines. In contrast, 525p (p: progressive) is a high-density signal with double the number of scan lines. ■ NTSC NTSC is a video signal system (525 lines, 30 frames per second) used in North America, Central America, a number of South American countries, and some Asian countries, including Japan. ■ PAL PAL is a video signal system (625 lines, 25 frames per second) used in the United Kingdom, much of the rest of western Europe, several South American countries, some Middle East and Asian countries, several African countries, Australia, New Zealand, and other Pacific island countries. 90