Yamaha GW10 Owner's Manual - Page 32
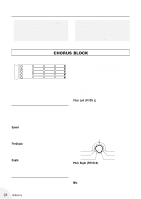
Chorus Block - harmony
 |
View all Yamaha GW10 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
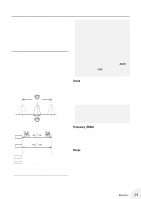
HINT - ABOUT THE OUTPUT LEVEL s Since the Output parameter of the Distortion block determines the loudness of the overall sound, the Distortion block is placed first in the effect chain (except when the Wah effect is used; see illustration in the SYSTEM OVERVIEW section on page 8). In general, you should set Output so that the level of the sound is constant, even when turning the Distortion block on and off. If the Output parameter is set too high or low, you may get unwanted sudden jumps or drops in the level of the sound when turning Distortion on and off. Moreover, if Output is set to the minimum, you won't get any sound at all. s CHORUS BLOCK CHO CHORUS P . SHIFT WAH EQ AMP SPEED PITCH L SENSE LOW TYPE FEEDBACK PITCH R FREQ MID TONE DEPTH MIX RANGE HIGH MIX The Chorus block features a wide range of modulation and tone control effects, including Chorus, Pitch Shift, Wah, Equalizer, and Amp Simulator. Chorus Chorus uses modulation of the pitch and separation of the signal into stereo to greatly enhance the sound, generally making it richer, fatter and warmer. Speed Determines the speed of the pitch modulation. Settings higher than around 4:00 produce very high speed modulation for special effects. Feedback Determines the amount of Chorus signal that fed back again to the Chorus input. Higher values result in a stronger, flanger-like sound. Depth Determines the depth of the pitch modulation, or how widely the pitch is varied. Pitch Shift Pitch Shift lets you change the pitch of the sound, up to an octave above or below the pitch of the input signal. Since the effect is stereo, you can set the 28 Reference amount of pitch shift independently for the left and right channels, creating three separate pitches (including the original direct signal). One application for this would be to create a natural, spacious stereo chorus effect in which the left and right pitches are detuned slightly relative to the direct sound. Other applications include setting the pitch shift to an octave below or above (to make a six-string guitar sound like a twelve-string), or setting the pitch to other intervals (such as a fourth or fifth) to create instant harmonies and fill out the sound. Pitch Left (PITCH L) Determines the amount of pitch shift for the left channel, up to one octave above or below the input pitch. The 12:00 position on the dial corresponds to unison pitch, while the pitch can be continuously detuned between the 9:00 and 3:00 positions. Fixed pitch shifts are available past those positions: an octave down at 7:00, a 5th down at 8:00, a 4th down at around 9:00, a 4th up at around 3:00, a 5th up at 4:00, and an octave up at 5:00. Unison pitch detuned detuned 4th down 5th down octave down 4th up 5th up octave up Pitch Right (PITCH R) Determines the amount of pitch shift for the right channel, up to one octave above or below the input pitch. (The settings are the same as in Pitch Left above.) Mix Determines the level of the Pitch Shift sound. The minimum setting corresponds to 0%, or no