ZyXEL MES3500-24F User Guide - Page 186
Multicast
 |
View all ZyXEL MES3500-24F manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
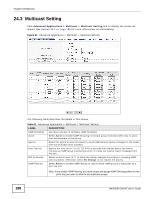
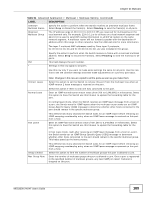
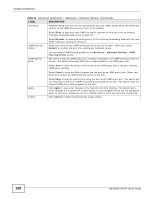
CHAPTER 24 Multicast This chapter shows you how to configure various multicast features. 24.1 Multicast Overview Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender to 1 recipient) or Broadcast (1 sender to everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to just a group of hosts on the network. IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. Refer to RFC 1112, RFC 2236 and RFC 3376 for information on IGMP versions 1, 2 and 3 respectively. 24.1.1 IP Multicast Addresses In IPv4, a multicast address allows a device to send packets to a specific group of hosts (multicast group) in a different subnetwork. A multicast IP address represents a traffic receiving group, not individual receiving devices. IP addresses in the Class D range (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255) are used for IP multicasting. Certain IP multicast numbers are reserved by IANA for special purposes (see the IANA website for more information). 24.1.2 IGMP Filtering With the IGMP filtering feature, you can control which IGMP groups a subscriber on a port can join. This allows you to control the distribution of multicast services (such as content information distribution) based on service plans and types of subscription. You can set the Switch to filter the multicast group join reports on a per-port basis by configuring an IGMP filtering profile and associating the profile to a port. 24.1.3 IGMP Snooping The Switch can passively snoop on IGMP packets transferred between IP multicast routers/switches and IP multicast hosts to learn the IP multicast group membership. It checks IGMP packets passing through it, picks out the group registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly. IGMP snooping allows the Switch to learn multicast groups without you having to manually configure them. The Switch forwards multicast traffic destined for multicast groups (that it has learned from IGMP snooping or that you have manually configured) to ports that are members of that group. IGMP snooping generates no additional network traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce multicast traffic passing through your Switch. MES3500-24/24F User's Guide 186