ZyXEL NWA1121-NI User Guide - Page 15
Ways to Manage the NWA1121-NI - firmware
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA1121-NI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
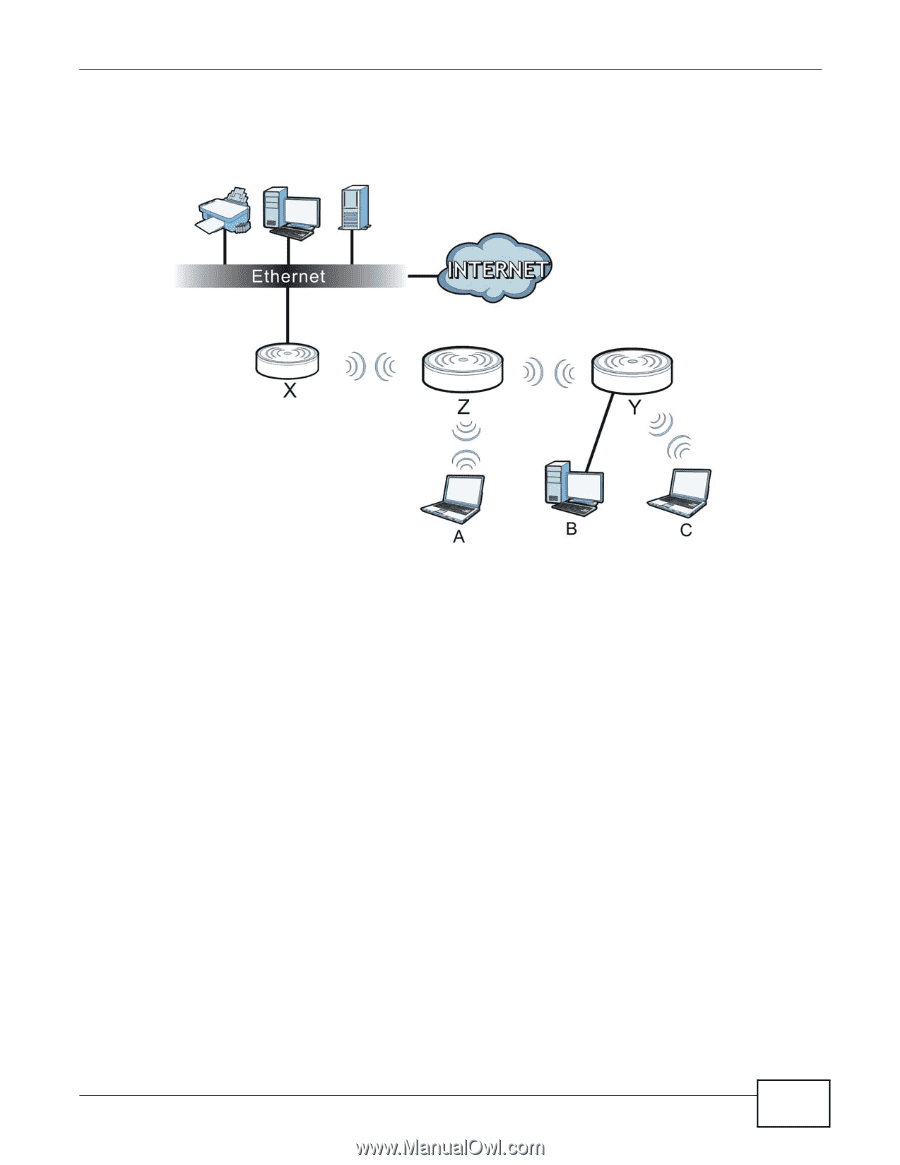
Chapter 1 Introducing the NWA1121-NI between associated wireless clients and the wired LAN. Clients A, B and C access the AP and the wired network behind the AP throught repeaters Z and Y. Figure 4 Repeater Application When the NWA1121-NI is in Repeater mode, universal repeater security between the NWA1121-NI and other repeater is independent of the security between the wireless clients and the AP or repeater. If you do not enable universal repeater security, traffic between APs is not encrypted. When universal repeater security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See Section 6.6 on page 74 for more details. Once the security settings of peer sides match one another, the connection between devices is made. At the time of writing, universal repeater security is compatible with the NWA1121-NI only. 1.3 Ways to Manage the NWA1121-NI Use any of the following methods to manage the NWA1121-NI. • Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the NWA1121-NI using a (supported) web browser. • FTP (File Transfer Protocol) for firmware upgrades and configuration backup and restore. • SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). The device can be monitored by an SNMP manager. NWA1121-NI User's Guide 15