Fujitsu MHM2150AT Manual/User Guide - Page 63
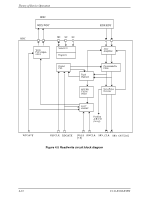
Command processing during self-calibration, 4.6 Read/write Circuit
 |
View all Fujitsu MHM2150AT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
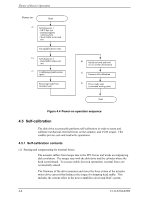
Theory of Device Operation Table 4.1 Self-calibration execution timechart Time elapsed 1 At power-on 2 About 5 minutes 3 About 5 minutes 4 About 10 minutes 5 About 10 minutes 6 About 15 minutes 7 About 15 minutes 8 . . Every about 30 . minutes . Time elapsed (accumulated) Initial calibration About 5 minutes About 10 minutes About 20 minutes About 30 minutes About 45 minutes About 60 minutes 4.5.3 Command processing during self-calibration If the disk drive receives a command execution request from the host while executing self-calibration according to the timechart, the disk drive terminates self-calibration and starts executing the command precedingly. In other words, if a disk read or write service is necessary, the disk drive positions the head to the track requested by the host, reads or writes data, and restarts calibration. This enables the host to execute the command without waiting for a long time, even when the disk drive is performing self-calibration. The command execution wait time is about maximum 40 ms. 4.6 Read/write Circuit The read/write circuit consists of the read/write preamplifier (HDIC), the write circuit, the read circuit, and the time base generator in the read channel (RDC). Figure 4.4 is a block diagram of the read/write circuit. 4.6.1 Read/write preamplifier (HDIC) HDIC equips a read preamplifier and a write current switch, that sets the bias current to the MR device and the current in writing. Each channel is connected to each data head, and HDIC switches channel by serial I/O. HDIC generates a write unsafe signal (WUS) when a write error occurs due to head short-circuits or head disconnection, that avoids error writing. 4-10 C141-E104-03EN