HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Installation Guide-6W100 - Page 15
Logging in through the OA module, Configuring the blade switch, Configuring an authentication method - blade switch configuration
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
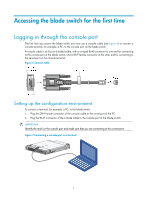
Press Enter at the prompt. When the command line prompt appears, you can configure the switch. For more information about the configuration, see "Configuring the blade switch." Logging in through the OA module To log in to the blade switch through the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator (OA) module: 1. Use a serial cable to connect the terminal (for example, a PC) to the serial port of the OA module. 2. Turn on the PC, run a terminal emulator program (for example, Windows XP HyperTerminal) on the PC, and set terminal parameters as follows: { Bits per second-9,600 { Data bits-8 { Parity-None { Stop bits-1 3. Press Enter and the login information appears. 4. Enter the username and password. OA prompt information appears on the login interface. 5. Enter the connect interconnect command, where the bay number argument specifies the slot number of the blade switch. 6. Press Enter. When the command line prompt appears, you can configure the switch. For more information about the configuration, see "Configuring the blade switch." Configuring the blade switch By default, the switch does not authenticate console login users. To increase system security and enable remote management: • Configure a login authentication method, for example, Telnet, SSH, or NMS. • Configure access services. Configuring an authentication method You can configure authentication on a user interface to control access to the switch. Table 2 describes the Telnet login authentication methods available for a VTY user interface. For more information about login authentication methods, see HP 6125 Blade Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide. Table 2 Telnet login authentication methods Authentication method None Password Characteristics Application scenarios Easy to configure, insecure Lab environments and extremely secure network environments Easy to configure, secure, providing flat user Environments that do not need granular management privilege management 11