HP ProLiant 1500 SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide - Page 142
Drive Mirroring RAID 1, RAID 1+0 or RAID 10.
 |
View all HP ProLiant 1500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 142 highlights
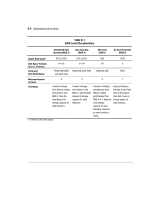
D-9 Drive Mirroring (RAID 1) Drive mirroring, also called RAID 1, is the highest performance fault tolerance method. RAID 1 is the only option offering fault tolerance protection if only two drives are installed or selected for an array. Drive mirroring creates fault tolerance by storing two sets of duplicate data on a pair of disk drives. Therefore, RAID 1 is the most expensive fault tolerance method because 50 percent of the drive capacity is used to store the redundant data. RAID 1 always requires an even number of drives. To improve performance in configurations with more than two drives, the data is striped across the drives. This is also referred to as RAID 1+0 or RAID 10. If a drive fails, the mirror drive provides a backup copy of the files and normal system operations are not interrupted. The mirroring feature requires a minimum of two drives and, in a multiple drive configuration (four or more drives), mirroring can withstand multiple simultaneous drive failures as long as the failed drives are not mirrored to each other. IMPORTANT: If two drives being mirrored to each other fail, the volume is failed and data loss may occur. DATA 12 3 4 DATA 12 3 4 WAR2-051.AI, 9-1.EPS Figure D-7. Drive Mirroring stores identical copy of the data SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide Writer: Pamela King Project: SMART-2DH Array Controller Reference Guide Comments: 295469-002 File Name: K-APPD.DOC Last Saved On: 2/27/98 12:06 PM COMPAQ CONFIDENTIAL - NEED TO KNOW REQUIRED