Adobe 65010248 Migration Guide - Page 27
Working with Appearances, and Styles
 |
UPC - 883919156484
View all Adobe 65010248 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
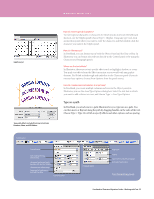
WORKING WITH APPEARANCES AND STYLES Working with Appearances and Styles The Appearance panel In FreeHand, you determine the properties of your objects in the Object Properties panel. In Illustrator, you use the Appearance panel to view and adjust the appearance attributes for an object, group, or layer. Appearance attributes are properties that affect the look of an object without altering its underlying structure. Appearance attributes include fills, strokes, transparency, and effects that you can apply to one object or multiple objects. You can then edit, remove, or toggle the visibility of attributes from within the Appearance panel in Illustrator CS4. You can even copy and paste inside the panel, so adding attributes to any object is fast and simple. In the Appearance panel, fills and strokes are listed in stacking order; top to bottom in the panel as they correlate to front to back in the artwork. Effects are listed from top to bottom in the order in which they are applied to the artwork. To display, choose Window > Appearance. Edit an effect such as Free Distort from within the Appearance panel. Use the eye icons to toggle attribute visibility Edit an attribute by simply clicking on a fill or stroke in the Appearance panel to access the corresponding options. If you wish to select all objects in your artwork that have certain attributes, you can use the Select menu to choose Same Appearance Attribute. Once you have selected objects with at least one common attribute, edit that attribute in the Appearance panel and see immediate results on all objects at once. The power of editing attributes in the Appearance panel lies in easy control of advanced effects without interacting with multiple panels. You can work in a more centralized manner, manipulating styles and complex combinations of attributes across many objects-all from one place. FreeHandtoIllustratorMigrationGuide-WorkingwithGraphics 27