D-Link DWC-2000 User Manual - Page 100
Ignore Broadcast, MAC Authentication, Authentication Type, Redirect, Redirect URL, Wireless ARP,
 |
View all D-Link DWC-2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
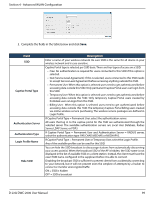
Section 4 - Advanced WLAN Configuration Field Ignore Broadcast VLAN MAC Authentication Authentication Type Redirect Redirect URL Wireless ARP Suppression Mode L2 Distributed Tunneling Mode Description If a wireless client broadcasts probe requests to all available SSIDs, this option controls whether the AP will respond to the probe request. ON = Prohibits the AP from responding to client probe requests. OFF = Allow the AP to respond to client probe requests. Enter a VLAN ID. Be sure this VLAN ID has been created (Network > VLAN > VLAN Setting) If enabled, wireless clients must be authenticated by the AP in order to connect to the network. To use MAC authentication, configure the client MAC addresses in one of the databases: Local or RADIUS. In the database, set a default action to either accept or deny that client or use the global action configured. MAC authentication is useful in networks that operate in Open mode to grant or deny access to clients with specific MAC addresses. MAC Authentication can also be used in conjunction with 802.1X security methods, in which the MAC Authentication is done prior to the 802.1X authentication. If Captive Portal Type = Permanent User and Authentication Server = RADIUS server, select the authentication type: PAP, CHAP, MSCHAP, or MSCHAPV2. Select the HTTP option in the Redirect field to redirect wireless clients to a custom Web page. When redirect mode is enabled, the user will be redirected to the URL you specify after the wireless client associates with an AP and the user opens a web browser to access the Internet. The custom Web page must be located on an external web server and might contain information such as the company logo and network usage policy. Note: The wireless client is redirected to the external Web server only once while it associated with the AP. Redirect functionality allows you to implement captive portal functionality; a captive portal is often used at Wi-Fi hotspots to provide branding for the hotspot provider and/ or display a legal disclaimer, which the user can click-through to access the Internet. HTTP=HTTP Redirect is enabled None=HTTP Redirect is disabled If Redirect = HTTP, enter the URL where all initial HTTP accesses should be redirected to. This field is accessible only when HTTP is selected as the redirect type. Enable the mode to allow APs to reduce the number of broadcasted ARP requests on the wireless interfaces. Reducing broadcasts helps conserve power on the wireless clients. The wireless clients that use power-save mode must wake up and use more power when they detect broadcast frames. Note: Enabling this feature slightly degrades AP packet forwarding performance due to extra packet filtering to find DHCP packets and extra processing for ARP request and reply packets. Networks that do not use IPv4 should not enable this feature. The distributed L2 tunneling mode supports L3 roaming for wireless clients without forwarding any data traffic to the Unified Wireless controller. Use the menu to enable or disable the mode. L2 tunneling is recommended when the Unified Wireless controller does not support hardware forwarding acceleration or hardware-based L2 tunnels. Note: 1 - When there is only one controller managing all APs and that controller goes down, all APs shut down their radios and the tunnel is terminated. After the controller recovers and the AP becomes managed again, the client that was previously tunneling traffic will re-associate and obtain an IP address on the network where its currently located. This IP address will be different from the IP address it was using when it was tunneling, and the traffic will not be tunneled. 2 - If the network has peer controllers and the tunnel is established between the APs managed by the peer controller then, when a controller managing the home AP fails, the controller managing the association AP detects the failure and terminates the tunnel. At this point the client is disassociated. When the client re-associates it obtains a new IP address. 3 - If the controller managing the association AP fails, then the scenario is the same as in item 1 above. The AP takes down all radios and the clients disassociate. D-Link DWC-2000 User Manual 100