Fujitsu MAN3367FC Manual/User Guide - Page 26
General Description
 |
View all Fujitsu MAN3367FC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
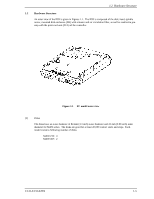
General Description 1.1 Standard Features (1) Compactness In a compact enclosure having the 3.5-inch HDD form factor, the IDD contains an FC-AL controller, which supports the Arbitrated Loop technology (FC-AL), a Fibre Channel technology defined by the related ANSI standard. (2) FC-AL standard The IDD provides not only FC-AL basic functions but also the following features: • Arbitration • Disconnection/Reconnection • Data bus parity • Command set which meets the logical specification of the SCSI CCS (Common Command Set for Direct Access Device) requirements (Rev. 4.B) The SCSI commands can manipulate data through logical block addressing regardless of the physical characteristics of the disk drive. This allows software to accommodate future expansion of system functions. (3) Dual-port support The IDD has two pairs of driver and receiver sets for the Fibre Channel to support dual-port connection. (4) High-speed data transfer The maximum data-transfer speed on the Fibre Channel loop is 212.5 MB/s. The large-capacity data buffer of the IDD enables the effective use of such high-speed data transfers available on the Fibre Channel loop. (5) Continuous block processing The addressing method of data blocks is logical block address. The initiator can access data by specifying block number in a logically continuous data space without concerning the physical structure of the track or cylinder boundaries. The continuous processing up to [64K-1] blocks in a command can be achieved, and IDD can perform continuous read/write operation when processing data blocks on several tracks or cylinder. 1-2 C141-E133-02EN