Fujitsu MAN3367FC Manual/User Guide - Page 32
Fujitsu MAN3367FC - Enterprise 36.7 GB Hard Drive Manual
 |
View all Fujitsu MAN3367FC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
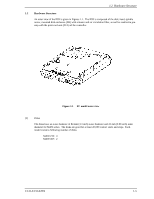
General Description (1) Loop configuration A port embedded with sending and receiving circuits uses differential signals to send and receive data on electric signal lines. A pair of signal lines is called a link. Since signals are sent in one direction on a link, the links in a system must be connected to form a loop. The FC-AL interface sends and receives data via nodes on the loop. Therefore, if a node connected to a loop is powered off or the interface signals of a node cannot be sent or received correctly, the loop does not work normally. A common solution preventing this problem from occurring is to add a port bypass circuit on the back plane of the system. BC in Figure 1.3 indicates the port bypass circuit. (2) Node addressing A specific device number called a SEL ID is assigned to each node on a Fibre Channel loop. The combination of signal levels on the back plane is used to define the SEL ID of a disk drive. The signal levels are sent on the seven signals (from SEL_0 to SEL_6) from CN1, which serves as an SCA interface connector. SEL_6 is the most significant bit (MSB), having a bit weight of the sixth power of 2, and SEL_0 is the least significant bit (LSB), having a bit weight of the zeroth power of 2. Any number from 0 (X'00) to 125 (X'7D') can be assigned as the SEL ID of a disk drive. 1-8 C141-E133-02EN