HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 116
Configuring MSTP, Planning an MSTP Application
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 116 highlights
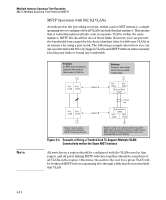
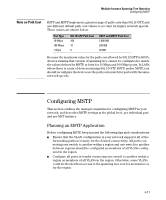
Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation Configuring MSTP Note on Path Cost RSTP and MSTP implement a greater range of path costs than 802.1D STP, and use different default path cost values to account for higher network speeds. These values are shown below. Port Type 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 1 Gbps 802.1D STP Path Cost 100 10 5 RSTP and MSTP Path Cost 2 000 000 200 000 20 000 Because the maximum value for the path cost allowed by 802.1D STP is 65535, devices running that version of spanning tree cannot be configured to match the values defined by MSTP, at least for 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps ports. In LANs where there is a mix of devices running 802.1D STP, RSTP, and/or MSTP, you should reconfigure the devices so the path costs match for ports with the same network speeds. Configuring MSTP This section outlines the main pre-requisites for configuring MSTP in your network, and describes MSTP settings at the global level, per individual port, and per MST instance. Planning an MSTP Application Before configuring MSTP, keep in mind the following tips and considerations: ■ Ensure that the VLAN configuration in your network supports all of the forwarding paths necessary for the desired connectivity. All ports connecting one switch to another within a region and one switch to another between regions should be configured as members of all VLANs configured in the region. ■ Configure all ports or trunks connecting one switch to another within a region as members of all VLANs in the region. Otherwise, some VLANs could be blocked from access to the spanning-tree root for an instance or for the region. 4-17