HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 158
show spanning-tree root-history, spanning-tree root-guard, history, spanning-tree priority
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 158 highlights
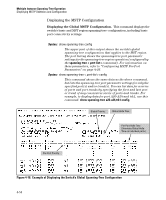
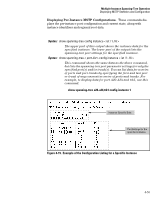
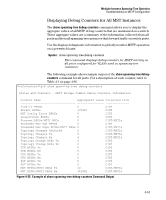
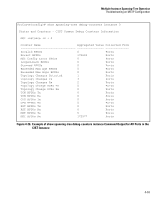
Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation Troubleshooting an MSTP Configuration ■ MST Instance (mst): Connects all static and (starting from release 13.x.x) dynamic VLANs assigned to a multiple spanning-tree instance. Syntax: show spanning-tree root-history This command displays the change history for the root bridge in the specified MSTP topology. The cst parameter displays the change history for the root bridge of a spanning-tree network, including MST regions and STP and RSTP bridges. The ist parameter displays the change history for the root bridge in the IST instance of an MST region. The mst parameter displays the change history for the root bridge in an MST instance, where is an ID number from 1 to 16. Use the show spanning-tree root-history command to view the number and dates of changes in the assignment of a root bridge. Possible intrusion into your MST network may occur if an unauthorized external device gains access to a spanning tree by posing as the root device in a topology. To prevent an MST port connected to the device from being selected as the root port in a topology, use the spanning-tree root-guard command. The following examples show sample output of the show spanning-tree roothistory command for different MSTP topologies. Note that in each example, the root bridge ID is displayed in the format: Where: ■ is the MSTP switch priority calculated for one of the following: • The IST (regional) root switch using the spanning-tree priority command • An MSTI root switch using the spanning-tree instance priority command ■ is the MAC address of the root (bridge) switch. 4-59