HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 180
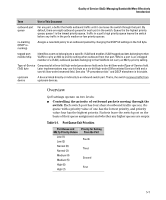
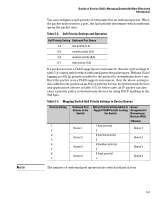
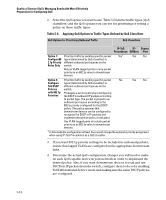
Table 5-2., QoS Priority Settings and Operation, Mapping Switch QoS Priority Settings to Device Queues
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 180 highlights
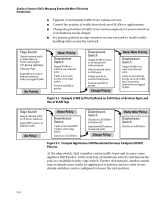
Note Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Introduction You can configure a QoS priority of 0 through 3 for an outbound packet. When the packet is then sent to a port, the QoS priority determines which outbound queue the packet uses: Table 5-2. QoS Priority Settings and Operation QoS Priority Setting Outbound Port Queue 1-2 low priority (1,2) 0-3 normal priority (3,4) 4-5 medium priority (5,6) 6-7 high priority (7,8) If a packet is not in a VLAN-tagged port environment, then the QoS settings in table 5-2 control only to which outbound queue the packet goes. Without VLAN tagging, no 802.1p priority is added to the packet for downstream device use. But if the packet is in a VLAN-tagged environment, then the above setting is also added to the packet as an 802.1p priority for use by downstream devices and applications (shown in table 5-3). In either case, an IP packet can also carry a priority policy to downstream devices by using DSCP-marking in the ToS byte. Table 5-3. Mapping Switch QoS Priority Settings to Device Queues Priority Setting 1 2 0 3 4 5 6 7 Outbound Port Queues in the Switch Queue 1 Queue 2 Queue 3 Queue 4 802.1p Priority Setting Added to Queue Tagged VLAN Packets Leaving Assignment in the Switch Downstream Devices With: 4 Queues 1 (low priority) 2 Queue 1 0 (normal priority) 3 Queue 2 4 (medium priority) 5 Queue 3 6 (high priority) 7 Queue 4 The number of outbound port queues in the switch is fixed at four. 5-9