HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 178
Overview, Controlling the priority of outbound packets moving through the, switch
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 178 highlights
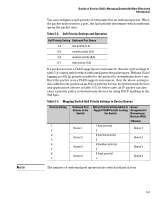
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Introduction Term Use in This Document outbound port queue For any port, a buffer that holds outbound traffic until it can leave the switch through that port. By default, there are eight outbound queues for each port in the switch. Queue 8 is the highest priority queue; queue 1 is the lowest priority queue. Traffic in a port's high priority queue leaves the switch before any traffic in the port's medium or low priority queues. re-marking (DSCP remarking) Assigns a new QoS policy to an outbound packet by changing the DSCP bit settings in the ToS byte. tagged port membership Identifies a port as belonging to a specific VLAN and enables VLAN-tagged packets belonging to that VLAN to carry an 802.1p priority setting when outbound from that port. Where a port is an untagged member of a VLAN, outbound packets belonging to that VLAN do not carry an 802.1p priority setting. Type-of-Service Comprised of a three-bit (high-order) precedence field and a five-bit (low-order) Type-of-Service field. (ToS) byte Later implementations may use this byte as a six-bit (high-order) Differentiated Services field and a two-bit (low-order) reserved field. See also "IP-precedence bits" and DSCP elsewhere in this table. upstream device A device linked directly or indirectly to an inbound switch port. That is, the switch receives traffic from upstream devices. Overview QoS settings operate on two levels: ■ Controlling the priority of outbound packets moving through the switch: Each switch port has four shared outbound traffic queues; the queue with a priority value of one has the lowest priority, and priority value four has the highest priority. Packets leave the switch port on the basis of their queue assignment and whether any higher queues are empty: Table 5-1. Port Queue Exit Priorities Port Queue and 802.1p Priority Values Low (1) Low (2) Normal (0) Normal (3) Medium (4) Medium (5) High (6) High (7) Priority for Exiting From the Port Fourth Third Second First 5-7