HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management G - Page 190
diff-services, Example Showing Codepoints Available for Direct 802.1p Priority
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 190 highlights
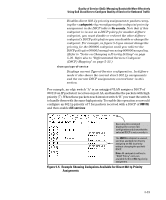
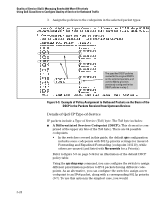
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Using QoS Classifiers to Configure Quality of Service for Outbound Traffic Disables direct 802.1p priority assignment to packets carrying the < codepoint > by reconfiguring the codepoint priority assignment in the DSCP table to No-override. Note that if this codepoint is in use as a DSCP policy for another diffserv codepoint, you must disable or redirect the other diffserv codepoint's DSCP policy before you can disable or change the codepoint. For example, in figure 5-5 you cannot change the priority for the 000000 codepoint until you redirect the DSCP policy for 000001 away from using 000000 as a policy. (Refer to "Notes on Changing a Priority Setting" on page 5-36. Refer also to "Differentiated Services Codepoint (DSCP) Mapping" on page 5-33.) show qos type-of-service Displays current Type-of-Service configuration. In diffserv mode it also shows the current direct 802.1p assignments and the current DSCP assignments covered later in this section. For example, an edge switch "A" in an untagged VLAN assigns a DSCP of 000110 on IP packets it receives on port A6, and handles the packets with high priority (7). When these packets reach interior switch "B" you want the switch to handle them with the same high priority. To enable this operation you would configure an 802.1p priority of 7 for packets received with a DSCP of 000110, and then enable diff-services: Executing this command displays the current ToS configuration and shows that the selected DSCP is not currently in The 000110 codepoint is unused, and thus available for directly assigning an 802.1p priority without changing the packet's DSCP. Note: All codepoints without a "DSCP Policy" entry are available for direct 802.1p priority assignment. Figure 5-5. Example Showing Codepoints Available for Direct 802.1p Priority Assignments 5-19