HP OMEN 15.6 Maintenance and Service Guide - Page 37
Generating static electricity, Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment, IMPORTANT
 |
View all HP OMEN 15.6 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
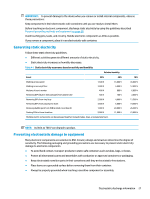
IMPORTANT: To prevent damage to the device when you remove or install internal components, observe these precautions: Keep components in their electrostatic-safe containers until you are ready to install them. Before touching an electronic component, discharge static electricity by using the guidelines described Personal grounding methods and equipment on page 28. Avoid touching pins, leads, and circuitry. Handle electronic components as little as possible. If you remove a component, place it in an electrostatic-safe container. Generating static electricity Follow these static electricity guidelines. ● Different activities generate different amounts of static electricity. ● Static electricity increases as humidity decreases. Table 4-1 Static electricity occurrence based on activity and humidity Relative humidity Event 55% 40% Walking across carpet Walking across vinyl floor Motions of bench worker Removing DIPs (dual in-line packages) from plastic tube 7,500 V 3,000 V 400 V 400 V 15,000 V 5,000 V 800 V 700 V Removing DIPs from vinyl tray Removing DIPs from polystyrene foam Removing bubble pack from PCB (printed circuit board) Packing PCBs in foam-lined box 2,000 V 3,500 V 7,000 V 5,000 V 4,000 V 5,000 V 20,000 V 11,000 V Multiple electric components can be packaged together in plastic tubes, trays, or polystyrene foam. 10% 35,000 V 12,000 V 6,000 V 2,000 V 11,500 V 14,500 V 26,500 V 21,000 V NOTE: As little as 700 V can degrade a product. Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment Many electronic components are sensitive to ESD. Circuitry design and structure determine the degree of sensitivity. The following packaging and grounding precautions are necessary to prevent static electricity damage to electronic components. ● To avoid hand contact, transport products in static-safe containers such as tubes, bags, or boxes. ● Protect all electrostatic parts and assemblies with conductive or approved containers or packaging. ● Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free stations. ● Place items on a grounded surface before removing them from their container. ● Always be properly grounded when touching a sensitive component or assembly. Electrostatic discharge information 27