Konica Minolta bizhub PRESS C1070/C1070P bizhub PRESS C1070/C1070P/C1060/bizhu - Page 108
Convenient Use of Scan Function (Scan to SMB), Step 1: Prepare the destination computer
 |
View all Konica Minolta bizhub PRESS C1070/C1070P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 108 highlights
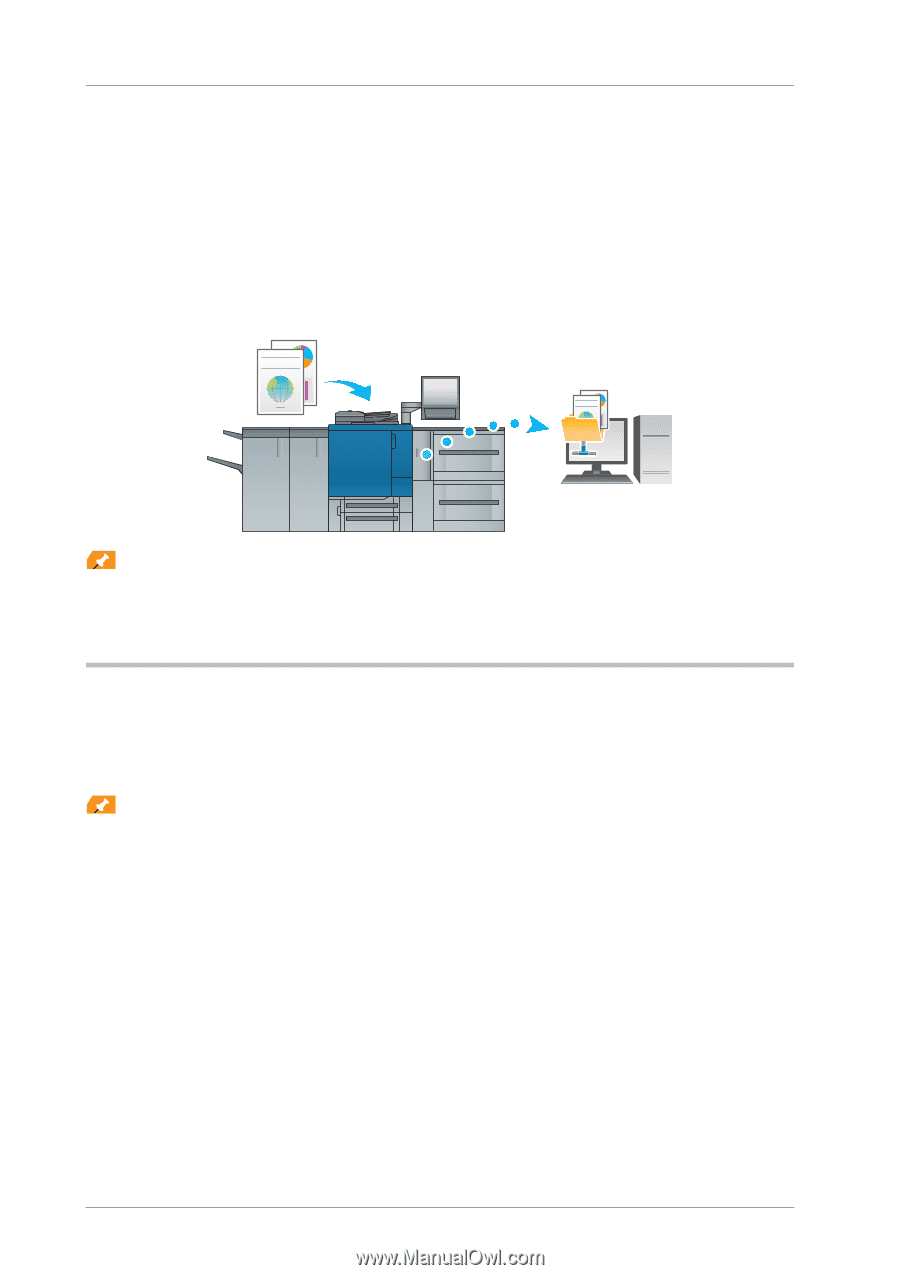
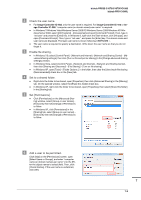
7.3 Convenient Use of Scan Function (Scan to SMB) 7.3 Convenient Use of Scan Function (Scan to SMB) You can send the scanned original data as an E-mail attachment, or send it to a shared computer (SMB server) or the FTP server. This section describes the function (Scan to SMB) to send data to the SMB server. SMB transmission is a function that converts the original data scanned on this machine to a computer-compatible file and sends the converted data to a target computer or a shared folder on the server. You can store a handout original as digital data using this function. Also, you can send data to your computer and the file server used for daily file transfer in order to share it. Tips Tips Mac OS X 10.7 or later does not support the Scan to SMB function. Instead, use Scan to FTP. For details, refer to the HTML User's Guide. Step 1: Prepare the destination computer In Step 1, execute the following tasks: - To check the destination computer name and accessible user name. - To create a destination folder and to start sharing. In a Windows environment. Tips Tips To carry out this task, the computer's administrator privilege is required. " In [System Properties] or [System], check the computer name displayed in [Computer name]. - In Windows 7/Windows Vista/Windows Server 2008 R2/Windows Server 2008/Windows XP/Windows Server 2003, right-click [Computer], then click [Properties] to display [System Properties]. - In Windows 8, right-click the Start window, click [All apps]. And right-click [Computer], then click [Properties] to display [System Properties]. - The computer name is required to specify a destination. Write down the computer name so that you do not forget it. - In Windows XP, you can check the user name in [System Properties]. 7-8