Netgear RM356 RM356 Reference Manual - Page 74
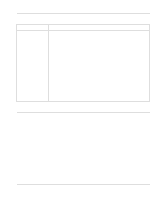
Static Route Setup, This menu is Menu 12.1, the Edit IP Static Route menu.
 |
UPC - 606449002263
View all Netgear RM356 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 74 highlights
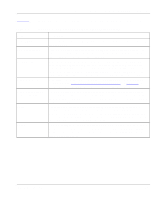
Reference Guide for the Model RM356 Modem Router Table 7-2. Menu 11.3 - Remote Node Network Layer Options Fields (continued) Field RIP: RIP Direction RIP Version Description This parameter determines how the router handles RIP (Routing Information Protocol). If set to Both (default), the router broadcasts its routing table to other routers and incorporates RIP broadcasts by other routers into its routing table. If set to In Only, the router will not broadcast its routing table but will accept RIP information from other routers. If set to Out Only, the router broadcasts its routing table, but it ignores any RIP broadcast packets that it receives. If set to None, the router does not participate in any RIP exchange with other routers. Usually, you should leave this parameter at the default (Both) and let RIP propagate the routing information automatically. This field determines which version of RIP (Routing Information Protocol) will be used by the router. The following RIP options are supported by the Model RM356 Modem Router: • RIP-1-The router will accept and send RIP-1 messages only. • RIP-2B-The router will accept RIP-1 and RIP-2 messages (both broadcast and multicast) and send RIP-2 messages in broadcast format. • RIP-2M-The router will accept RIP-1 and RIP-2 messages (both broadcast and multicast) and send RIP-2 messages in multicast format. For most applications, the recommended version is RIP-2B. Select RIP-1 if other connected routers or workstations do not support RIP-2. Select RIP-2M only in a pure RIP-2 environment. Static Route Setup On a directly connected internetwork, RIP usually handles the routing automatically. However, RIP cannot propagate across isolated networks, as in the case before a connection is made between two subnetworks using one Class C IP address. Without a route, no packets can be forwarded to their destinations. A static route is used to resolve this problem by providing the router with some static routing information. When you configure for Internet access or a remote node, a static route is implicitly created by the router. Under normal circumstances, the router has adequate routing information after you configure the Internet access and remote nodes, and you do not need to configure additional static routes. You must configure static routes only for unusual cases (for example, subnetting). To view the routes in the routing table, go to the Command Interpreter Mode (Menu 24.8) and type "ip route stat." After viewing the table, type "exit" to return to the menus. To create additional static routes for IP, use Menu 12 - Static Route Setup. Select an unused number from the menu, and a new menu opens. This menu is Menu 12.1, the Edit IP Static Route menu. 7-4 TCP/IP Configuration