Nokia 3590 Nokia 3590 User Guide in English - Page 128
Your WAP browser, • Notes on mobile Internet access
 |
UPC - 844602105455
View all Nokia 3590 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 128 highlights
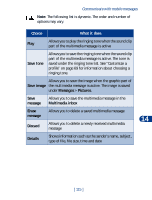
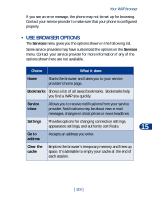
15 Your WAP browser Your phone has a built-in browser you can use to connect to selected services on the mobile Internet. You can view weather reports, check news or flight times, view financial information, make online purchases and much more. Your WAP browser • NOTES ON MOBILE INTERNET ACCESS This section gives a brief overview of mobile Internet technology. Technology background WAP A technology called Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is to mobile devices what the World Wide Web (WWW) is to personal computers. The mobile community began developing WAP several years ago to provide access to Internet sites designed for mobile users. Today, most WAP sites are made up of text and hyperlinks. Some pages 15 even contain low-resolution graphics, or require data input. Your service provider and others are free to design WAP sites as they choose, so the sites are as variable as Web pages on the Internet. Internet content on your personal computer is called a "web page." Internet content on your mobile phone is called a "page," "WAP card," or a "Deck of cards." GPRS General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a technology used to send and receive data via short bursts or packets over the wireless network. GPRS allows you to stay connected to the Internet. This feature allows for faster downloads of information and no time spent completing a dial-up connection. Applications using GPRS include the WAP browser and text messaging. [ 117 ]