Synology SA3200D Synology High Availability SHA User Guide for DSM 7.0 - Page 38
Split-brain, Resolve a split-brain error
 |
View all Synology SA3200D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
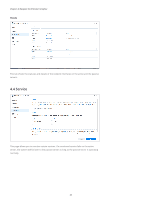
Chapter 4: Navigate the SHA User Interface 4.7 Split-brain When a high-availability cluster is functioning normally, only one of the hosts should act as the active server. The passive server detects the active server via the Heartbeat and the Cluster connections. You can set up multiple paths to connect the hosts to the data network to achieve data redundancy, but if the Heartbeat connection and the primary Cluster connection were both to fail, both servers may attempt to assume the role of the active server and result in a "split-brain" error. In this case, connections to the IP addresses of the high-availability cluster will be redirected to either of the two servers, causing inconsistent data to be written. Once either of the connections is reconnected, the system will detect the split-brain error and the data inconsistency between the hosts. If you want to simulate a split-brain error on your SHA cluster, refer to the Split-brain error simulation and solutions section of Chapter 3.3: Tests and simulations. Resolve a split-brain error 1. Reconnect the Heartbeat and Cluster connections. 2. Connect to either of the servers with the cluster IP address and open Synology High Availability. 3. To view the differences in the data on the two servers before resolving the split-brain error, go to the Split-brain page and select the shared folder you want to compare. • The system may take some time to check the files. If you need to solve the split-brain error as soon as possible, skip this step and select Keep all data of both servers in the next step. To compare the data, follow the instructions in this article. 4. Click Manage > Resolve split-brain errors on the Cluster page and follow the onscreen instructions. There are two options to choose from:1 • Keep all data of both servers: Choose one host as the new active server and remove the other. The new active server will still be in the cluster. The removed host will keep its data and return to standalone status. A full data synchronization is required the next time you add a passive server. • Keep data from only one of the servers: Choose one of the hosts as the new active server. The system will sync the data and settings on the new active server to the new passive server.2 Notes: 1. Make sure both hosts in the cluster are powered on before you choose the new active server when resolving the error. Shutting down the cluster does not solve the error. The split-brain error will remain until you address it using the methods mentioned in this article. 2. The changes made on the passive server during the split-brain will be lost if you choose this option. 36