TP-Link TL-SL2218 TL-SL2218 V1 User Guide - Page 10
Introduction, LAG: Con Link Aggregation Group. LAG is to combine
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SL2218 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
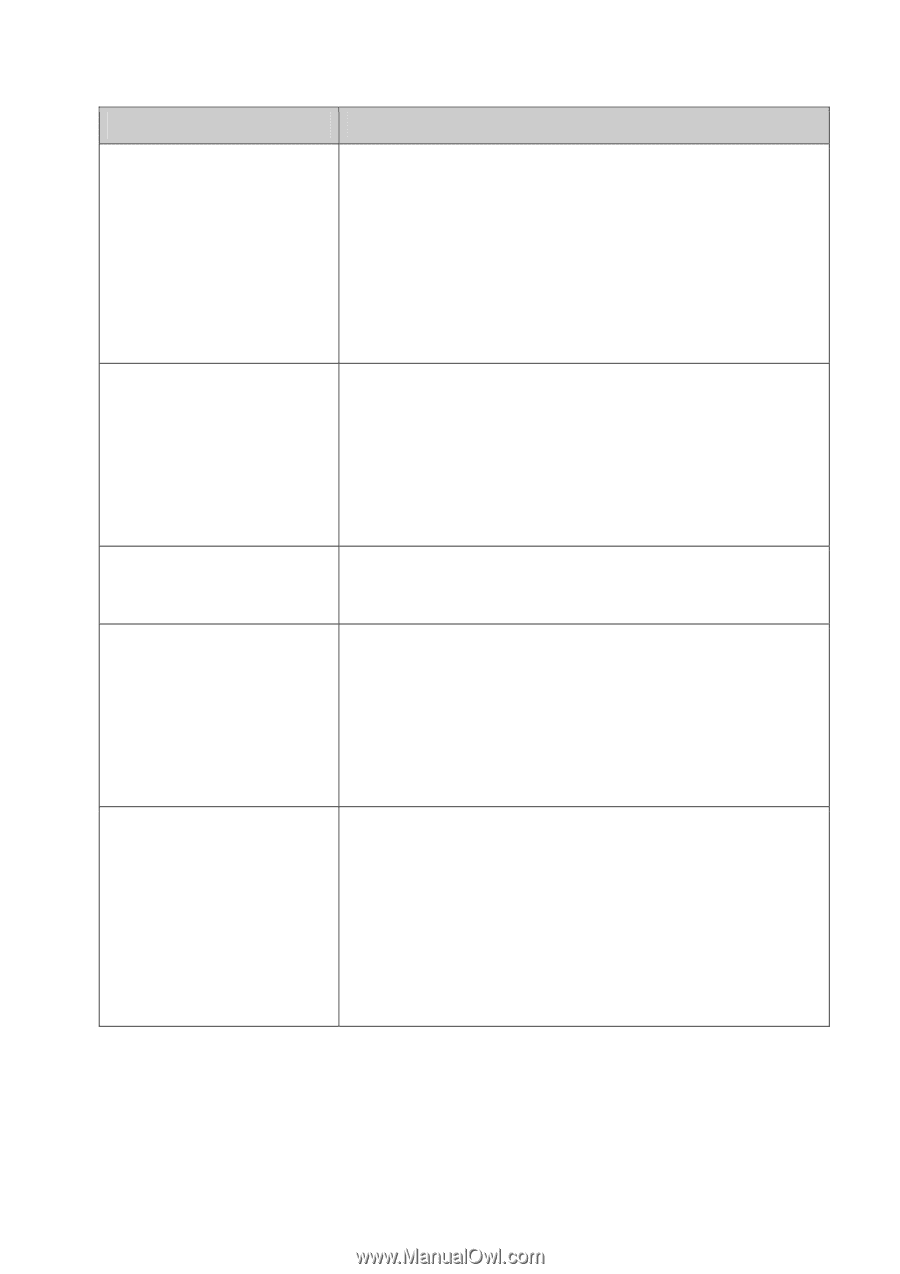
Chapter Chapter 4 System Chapter 5 Switching Chapter 6 VLAN Chapter 7 Spanning Tree Chapter 8 Multicast Introduction This module is used to configure system properties of the switch. Here mainly introduces: z System Info: Configure the description, system time, Daylight Saving Time and network parameters of the switch. z User Management: Configure the user name and password for users to log on to the Web management page with a certain access level. z System Tools: Manage the configuration file of the switch. z Access Security: Access Security is configured to control the users logging on to the Web management page. This module is used to configure basic functions of the switch. Here mainly introduces: z Port: Configure the basic features for the port. z LAG: Configure Link Aggregation Group. LAG is to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth data path. z Traffic Monitor: Monitor the traffic of each port. z MAC Address: Configure the address table of the switch. This module is used to configure VLANs to control broadcast in LANs. Here mainly introduces: z 802.1Q VLAN: Configure port-based VLAN. This module is used to configure spanning tree function of the switch. Here mainly introduces: z STP Config: Configure and view the global settings of spanning tree function. z Port Config: Configure CIST parameters of ports. z MSTP Instance: Configure MSTP instances. z STP Security: Configure protection function to prevent devices from any malicious attack against STP features. This module is used to configure multicast function of the switch. Here mainly introduces: z IGMP Snooping: Configure global parameters of IGMP Snooping function, port properties, VLAN and multicast VLAN. z Multicast IP: Configure multicast IP table. z Multicast Filter: Configure multicast filter feature to restrict users ordering multicast programs. z Packet Statistics: View the multicast data traffic on each port of the switch, which facilitates you to monitor the IGMP messages in the network. 3