TP-Link TL-SL2218 TL-SL2218 V1 User Guide - Page 37
LAG, 5.2.1 LAG Table
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SL2218 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
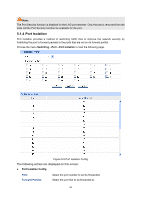
¾ Port Isolation List Port: Forward Portlist: Display the port number. Display the forwardlist. 5.2 LAG LAG (Link Aggregation Group) is to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth data path, so as to implement the traffic load sharing among the member ports in the group and to enhance the connection reliability. For the member ports in an aggregation group, their basic configuration must be the same. The basic configuration includes STP, QoS, VLAN, port attributes, MAC Address Learning mode and other associated settings. The further explains are following: z If the ports, which are enabled for the STP, QoS, Port Isolation and Port Configuration (Speed and Duplex, Flow Control), are in a LAG, their configurations should be the same. z The ports, which are enabled for the Port Security, Port Mirror, MAC Address Filtering, and Static MAC Address Binding, can not be added to the LAG. If the LAG is needed, you are suggested to configure the LAG function here before configuring the other functions for the member ports. Tips: 1. Calculate the bandwidth for a LAG: If a LAG consists of the four ports in the speed of 1000Mbps Full Duplex, the whole bandwidth of the LAG is up to 8000Mbps (2000Mbps * 4) because the bandwidth of each member port is 2000Mbps counting the up-linked speed of 1000Mbps and the down-linked speed of 1000Mbps. 2. The traffic load of the LAG will be balanced among the ports according to the Aggregate Arithmetic. If the connections of one or several ports are broken, the traffic of these ports will be transmitted on the normal ports, so as to guarantee the connection reliability. The LAG function is implemented on the LAG Table and Static LAG configuration pages. 5.2.1 LAG Table On this page, you can view the information of the current LAG of the switch. Choose the menu Switching→LAG→LAG Table to load the following page. 30