TP-Link TL-SL2218 TL-SL2218 V1 User Guide - Page 109
Snmp
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SL2218 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
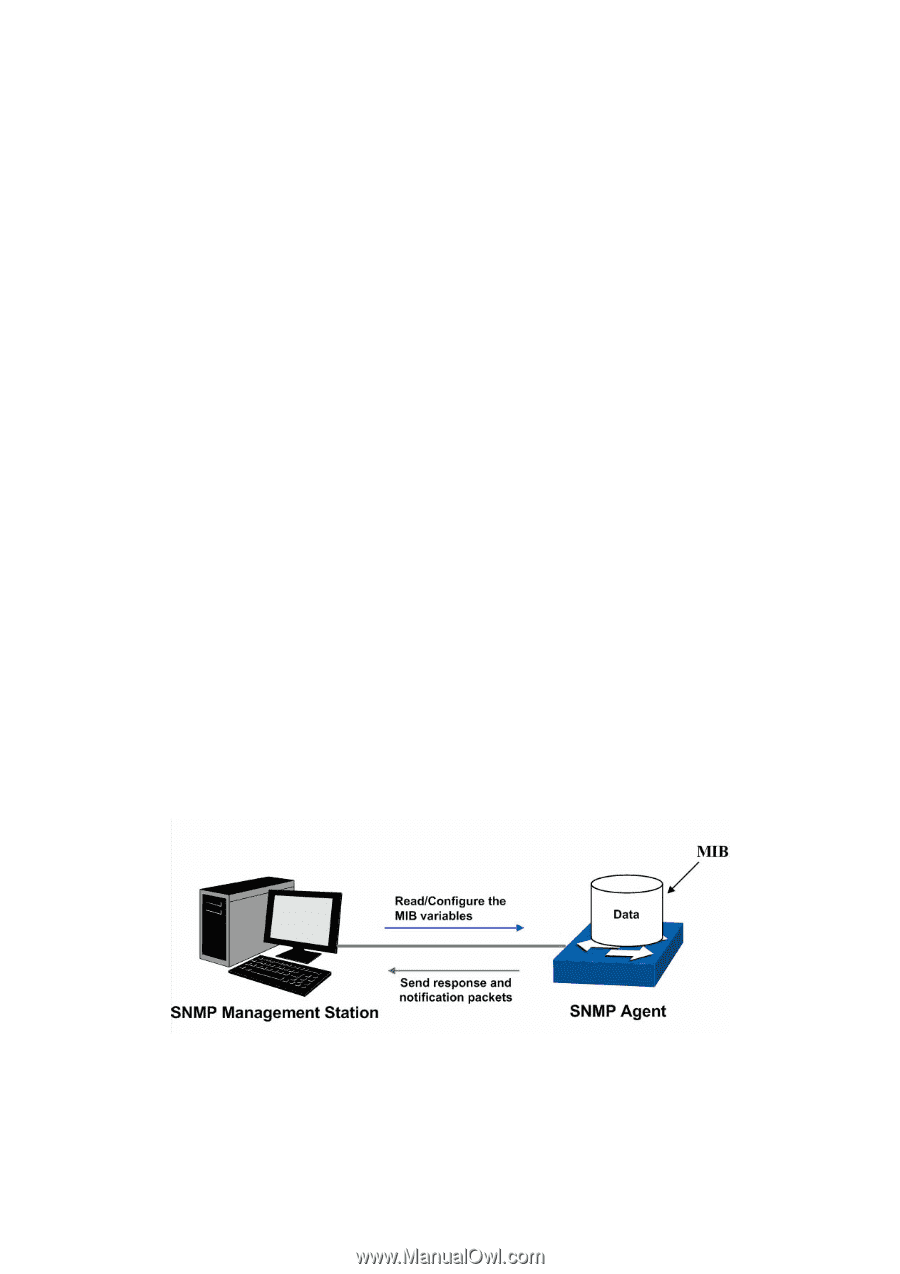
Chapter 10 SNMP ¾ SNMP Overview SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) has gained the most extensive application on the UDP/IP networks. SNMP provides a management frame to monitor and maintain the network devices. It is used for automatically managing the various network devices no matter the physical differences of the devices. Currently, the most network management systems are based on SNMP. SNMP is simply designed and convenient for use with no need of complex fulfillment procedures and too much network resources. With SNMP function enabled, network administrators can easily monitor the network performance, detect the malfunctions and configure the network devices. In the meantime, they can locate faults promptly and implement the fault diagnosis, capacity planning and report generating. ¾ SNMP Management Frame SNMP management frame includes three network elements: SNMP Management Station, SNMP Agent and MIB (Management Information Base). SNMP Management Station: SNMP Management Station is the workstation for running the SNMP client program, providing a friendly management interface for the administrator to manage the most network devices conveniently. SNMP Agent: Agent is the server software operated on network devices with the responsibility of receiving and processing the request packets from SNMP Management Station. In the meanwhile, Agent will inform the SNMP Management Station of the events whenever the device status changes or the device encounters any abnormalities such as device reboot. MIB: MIB is the set of the managed objects. MIB defines a few attributes of the managed objects, including the names, the access rights, and the data types. Every SNMP Agent has its own MIB. The SNMP Management station can read/write the MIB objects basing on its management right. SNMP Management Station is the manager of SNMP network while SNMP Agent is the managed object. The information between SNMP Management Station and SNMP Agent are exchanged through SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). The relationship among SNMP Management Station, SNMP Agent and MIB is illustrated in the following figure. Figure 10-1 Relationship among SNMP Network Elements ¾ SNMP Versions This switch supports SNMP v3, and is compatible with SNMP 1 and SNMP v2c. The SNMP versions adopted by SNMP Management Station and SNMP Agent should be the same. Otherwise, SNMP Management Station and SNMP Agent can not communicate with each other 102