ZyXEL B-320 User Guide - Page 21
Roaming, Infrastructure Network Example
 |
View all ZyXEL B-320 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
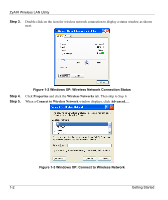
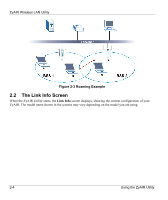
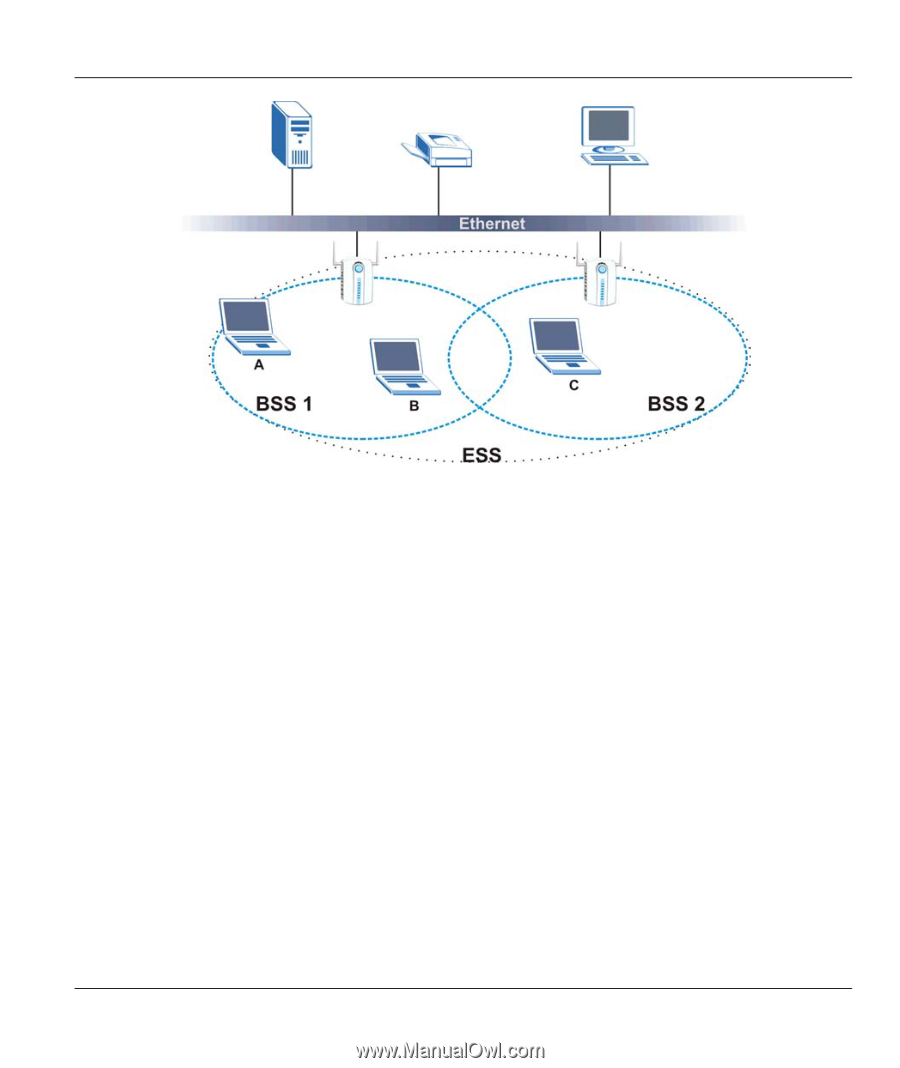
ZyAIR Wireless LAN Utility Figure 2-2 Infrastructure Network Example 2.1.5 Roaming Roaming is where in an infrastructure network, wireless clients are able to switch from one BSS to another as they move between coverage areas. During this period, the wireless client maintains an uninterrupted connection to the network. As the wireless client moves from place to place, it scans for the most appropriate AP depending on the signal strength, network utilization or other factors. The following figure depicts a roaming example. When wireless client B moves to position X, the ZyAIR in wireless client B automatically switches the channel to the one used by access point 2 in order to stay connected to the network. Using the ZyAIR Utility 2-3
ZyAIR Wireless LAN Utility
Using the ZyAIR Utility
2-3
Figure 2-2 Infrastructure Network Example
2.1.5 Roaming
Roaming is where in an infrastructure network, wireless clients are able to switch from one BSS to another
as they move between coverage areas. During this period, the wireless client maintains an uninterrupted
connection to the network. As the wireless client moves from place to place, it scans for the most
appropriate AP depending on the signal strength, network utilization or other factors.
The following figure depicts a roaming example. When wireless client B moves to position X, the ZyAIR
in wireless client B automatically switches the channel to the one used by access point 2 in order to stay
connected to the network.