HP EliteBook 8770w RAID User Guide - Page 17
Intel Rapid Recover Technology, Mirror update policies
 |
View all HP EliteBook 8770w manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
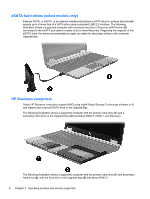
Intel Rapid Recover Technology Intel Rapid Storage Technology supports the following recovery features. Mirror update policies With Recovery, you can determine how often the mirror hard drive is updated: continuously or onrequest. When using the continuous update policy, data on the primary drive is simultaneously copied to the mirror drive as long as both drives are connected to the system. If you undock the computer while using the docking station's recovery drive, all new or revised data on the primary hard drive is automatically copied to the recovery hard drive when the notebook is redocked. This policy also allows for an unfinished mirroring operation to be completed if it was interrupted when you undocked the notebook. When using the update on-request policy, data on the primary hard drive is copied to the mirror hard drive only when you request it by selecting Update Recovery Volume in Recovery. After the request, only the new or updated files on the primary drive are copied to the mirror hard drive. Prior to updating the mirror hard drive, the on-request policy allows a file to be recovered if the corresponding file on the primary hard drive is corrupted. The on-request policy can also protect data on the mirror hard drive if the primary hard drive is attacked by a virus, provided you do not update the mirror hard drive after the virus attack. NOTE: You can change the mirror update policy at any time by right-clicking Modify Volume Update Policy. Automatic hard drive switching and rapid recovery If the primary hard drive fails, Recovery automatically switches to the mirrored drive without user intervention. Recovery displays a message to notify you of the primary hard drive failure. In the meantime, the computer can boot from the mirrored hard drive. When a new primary hard drive is installed and the computer is booted, Recovery's rapid recovery feature copies all mirrored data to the primary hard drive. NOTE: If using the update on request policy and the primary hard drive fails or a file on the primary hard drive becomes corrupted, all unmirrored data is lost. Simplified migration from RAID to non-RAID Users can migrate from a RAID 1 or Recovery volume to two non-RAID hard drives, called "breaking the array," by following the instructions in Resetting RAID drives to non-RAID on page 32. Migration from RAID 1 to Recovery is also supported. However, migration from RAID 0 to RAID 1 or from RAID 0 to a non-RAID primary hard drive is not supported. Intel Rapid Recover Technology 13