HP EliteBook 8770w RAID User Guide - Page 8
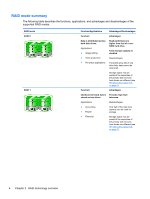
RAID mode summary, The following table describes the functions, applications
 |
View all HP EliteBook 8770w manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
RAID mode summary The following table describes the functions, applications, and advantages and disadvantages of the supported RAID modes. RAID levels RAID 0 RAID 1 Function/Applications Advantages/Disadvantages Function: Advantages: Data is distributed across both disk drives. Applications: ● Image editing ● Video production ● Pre-press applications Read performance is higher than that of a nonRAID hard drive. Total storage capacity is doubled. Disadvantages: The entire array fails if one drive fails; data cannot be recovered. Storage space may be wasted if the capacities of the primary and recovery hard drives are different (see HP SATA drive option kits on page 7). Function: Advantages: Identical (mirrored) data is Provides high fault stored on two drives. tolerance. Applications: ● Accounting ● Payroll ● Financial Disadvantages: Only half of the total drive capacity can be used for storage. Storage space may be wasted if the capacities of the primary and recovery hard drives are different (see HP SATA drive option kits on page 7). 4 Chapter 2 RAID technology overview