Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager User Manual - Page 34
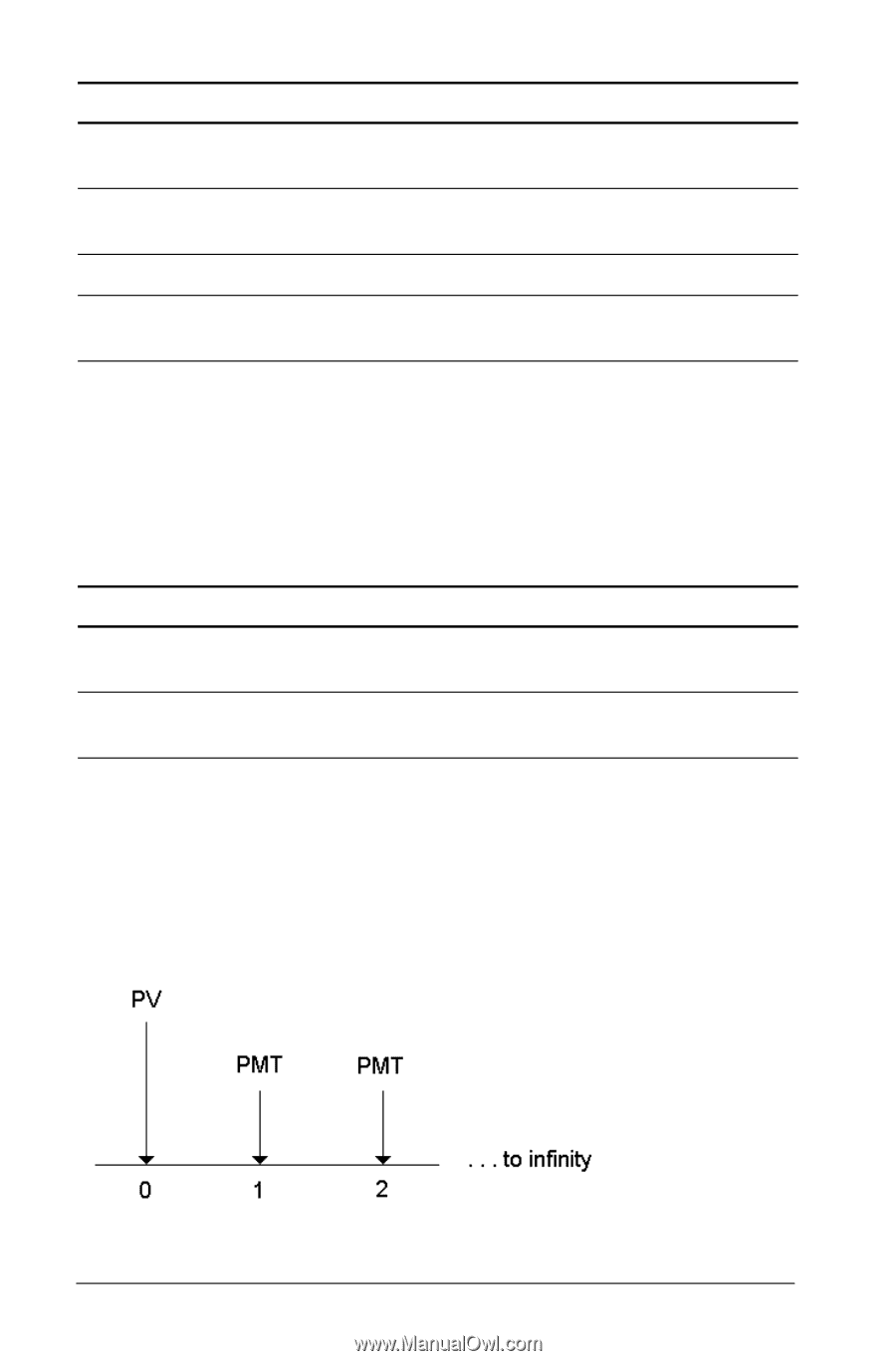
Example: Computing Perpetual Annuities, Perpetual ordinary annuity
 |
View all Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 34 highlights
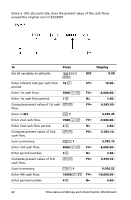
To Compute present value (ordinary annuity). Set beginning-of-period payments. Return to calculator mode. Compute present value (annuity due). Press % . Display PV= 122,891.34 & ] & V BGN & U % . 0.00 PV= 135,180.48 Answer: The present value of the savings is $122,891.34 with an ordinary annuity and $135,180.48 with an annuity due. Example: Computing Perpetual Annuities To replace bricks in their highway system, the Land of Oz has issued perpetual bonds paying $110 per $1000 bond. What price should you pay for the bonds to earn 15% annually? To Calculate the present value for a perpetual ordinary annuity. Calculate the present value for a perpetual annuity due. Press 110 6 15 2 N H 110 N Display 733.33 843.33 Answer: You should pay $733.33 for a perpetual ordinary annuity and $843.33 for a perpetual annuity due. A perpetual annuity can be an ordinary annuity or an annuity due consisting of equal payments continuing indefinitely (for example, a preferred stock yielding a constant dollar dividend). Perpetual ordinary annuity 30 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets