Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager User Manual - Page 65
Example: Computing Straight-Line Depreciation, Access Depreciation
 |
View all Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
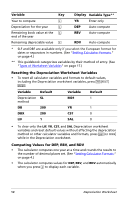
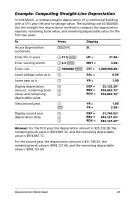
Example: Computing Straight-Line Depreciation In mid-March, a company begins depreciation of a commercial building with a 31½ year life and no salvage value. The building cost $1,000,000. Use the straight-line depreciation method to compute the depreciation expense, remaining book value, and remaining depreciable value for the first two years. To Access Depreciation worksheet. Enter life in years. Enter starting month. Enter cost. Leave salvage value as is. Leave year as is. Display depreciation amount, remaining book value, and remaining depreciable value. View second year. Display second year depreciation data. Press & p Display SL # 31.5 ! LIF = 31.50 # 3.5 ! M01 = 3.50 # 1000000 ! CST = 1,000,000.00 # SAL = 0.00 # YR = 1.00 # DEP = 25,132.28* # RBV = 974,867.72* # RDV = 974,867.72* # YR = 1.00 % YR = 2.00 # DEP = 31,746.03* # RBV = 943,121.69* # RDV = 943,121.69* Answer: For the first year, the depreciation amount is $25,132.28, the remaining book value is $974,867.72, and the remaining depreciable value is $974,867.72. For the second year, the depreciation amount is $31,746.03, the remaining book value is $943,121.69, and the remaining depreciable value is $943,121.69. Depreciation Worksheet 61