Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager User Manual - Page 35
Example: Computing Present Value of Variable Cash Flows, Because the term 1 + I/Y / 100
 |
View all Texas Instruments BA-20 Profit Manager manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 35 highlights
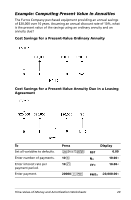
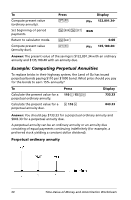
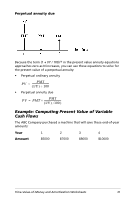
Perpetual annuity due Because the term (1 + I/Y / 100)-N in the present value annuity equations approaches zero as N increases, you can use these equations to solve for the present value of a perpetual annuity: • Perpetual ordinary annuity PV = (---I--/--Y-P---)-M---÷---T--1---0---0- • Perpetual annuity due PV = PMT + (---I--/--Y--P--)--M--⁄--1-T--0---0-----) Example: Computing Present Value of Variable Cash Flows The ABC Company purchased a machine that will save these end-of-year amounts: Year 1 2 3 4 Amount $5000 $7000 $8000 $10000 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets 31

Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets
31
Perpetual annuity due
Because the term (1 + I/Y / 100)
-
N
in the present value annuity equations
approaches zero as N increases, you can use these equations to solve for
the present value of a perpetual annuity:
•
Perpetual ordinary annuity
•
Perpetual annuity due
Example: Computing Present Value of Variable
Cash Flows
The ABC Company purchased a machine that will save these end-of-year
amounts:
Year
1
2
3
4
Amount
$5000
$7000
$8000
$10000
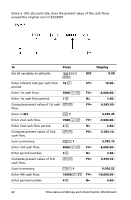
PV
PMT
I/Y
(
)
100
÷
---------------------------
=
PV
PMT
PMT
I/Y
(
)
100
)
⁄
----------------------------
+
=