Western Digital WDBACA0010BBK Instruction Manual - Page 83
Media Server, Network Share, Windows Shares
 |
UPC - 718037772370
View all Western Digital WDBACA0010BBK manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
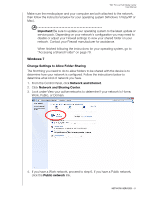
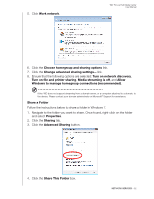
WD TV Live Hub Media Center User Manual Media Server This menu displays network attached UPnP media servers connected to your network and usage is optimized with DLNA compliant devices such as WD My Book Live personal cloud storage and other WD TV Live Hub media centers. The benefit of using a media server is that it aggregates the content together from the device that is hosting it. The media server hosts a list of supported file formats with metadata information that allows a client device like the media player to easily browse and play back the content. However, using a media server can restrict supported file types and you may not be able to see all the files stored in the media server. When using a Network Share, every file is presented to the media player and it does the content filtering based on what it can support. Follow the steps below under "Accessing a Shared Folder," selecting the name of your media server and referencing your media server documentation for password setup and administration if necessary. Network Share The media player supports Windows (SMB/CIFS), and Linux (NFS) network shares. Windows Shares Windows Shares uses Samba (also known as SMB/CIFS), a more common protocol among devices such as PC, NAS, and Mac (before Lion). If you want to simply discover and/or share a folder on the network to be accessed by the media player, Samba is a common method, especially for Windows. NETWORK SERVICES - 78