Adaptec 1405 User Guide - Page 52
How do SAS Devices Communicate?, What’s a Phy?, What’s a SAS Port?, narrow port, wide port
 |
View all Adaptec 1405 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
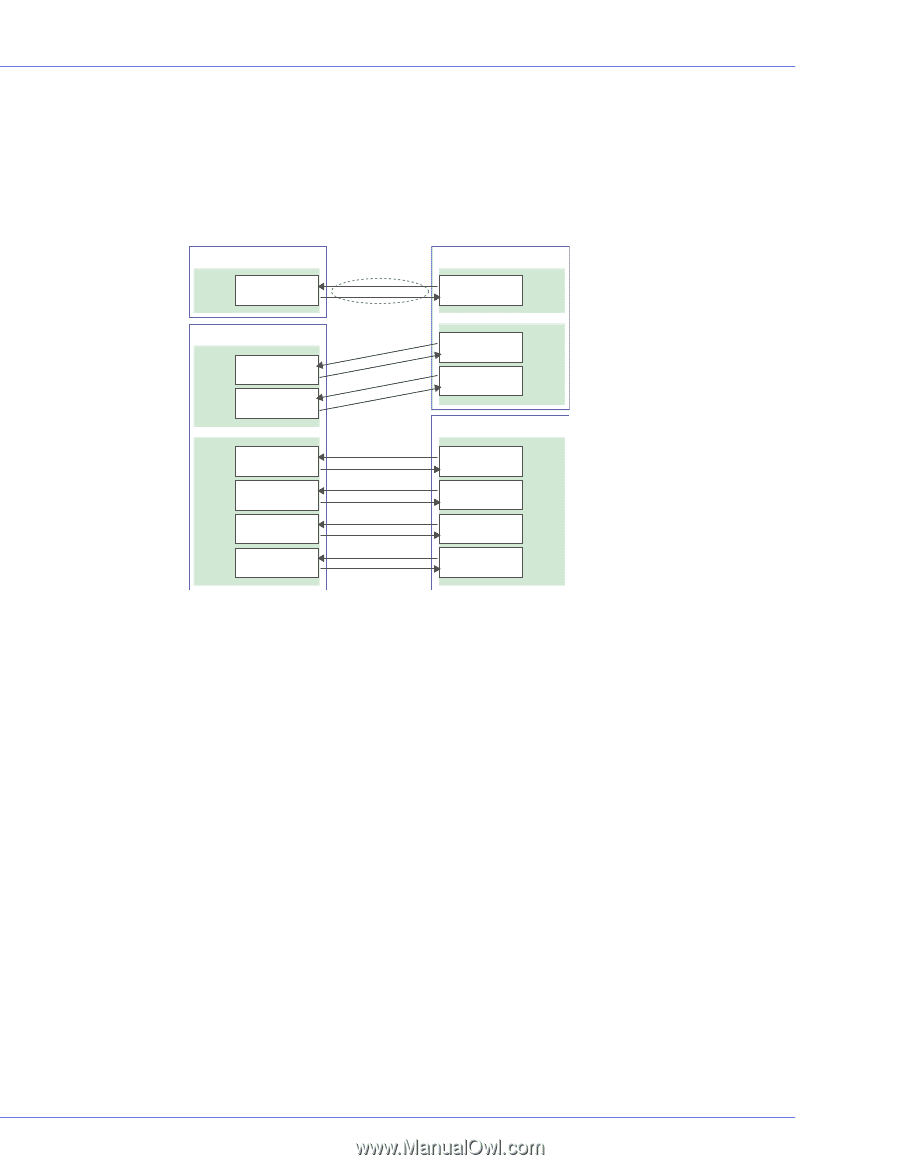
Chapter A: Introduction to SAS l 52 How do SAS Devices Communicate? SAS devices communicate with each other through links. A link is a physical connection between two phys. As shown in the following figure, SAS devices contain ports which contain phys (see next section), and each phy contains one transmitter and one receiver (one transceiver). A phy can belong to one port only. SAS Device SAS Device link Narrow Port Phy Receiver Transmitter Transmitter Receiver Phy Narrow Port SAS Device Wide Port Phy Receiver Transmitter Phy Receiver Transmitter Wide Port Phy Receiver Transmitter Phy Receiver Transmitter Phy Receiver Transmitter Phy Receiver Transmitter Transmitter Receiver Phy Transmitter Receiver Phy Wide Port SAS Device Transmitter Receiver Phy Transmitter Receiver Phy Transmitter Receiver Phy Transmitter Receiver Phy Wide Port What's a Phy? Phys are part of the physical communication connection between SAS devices. Each phy contains a transceiver that sends data back and forth between SAS devices. When a connection is formed between two end devices, a link is established from a phy in one port to a phy in the other port. As shown in the figure above, a wide port can support multiple independent links simultaneously. Phys are internal, within SAS connectors (see page 53). SAS cables physically connect one or more phys on one SAS device to one or more phys on another SAS device. What's a SAS Port? Note: Because the physical link between SAS devices is from phy to phy, rather than port to port, a port is more of a virtual concept, different from what is normally considered a port on other types of controllers and storage devices. A port is one or more phys. A narrow port contains one phy. A wide port typically contains four phys. Each port has its own unique SAS address (see page 53), and all the phys in a port share that same SAS address.