Campbell Scientific IRGASON IRGASON Integrated CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer - Page 41
IRGASON, Integrated CO, O Open-Path Gas Analyzer and 3D Sonic Anemometer,
 |
View all Campbell Scientific IRGASON manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 41 highlights
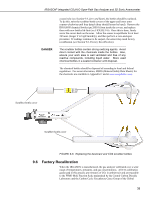
IRGASON® Integrated CO2/H2O Open-Path Gas Analyzer and 3D Sonic Anemometer NOTE Use mixtures of CO2 and ambient air for the CO2 span gas. The use of reference CO2 gas mixtures in pure nitrogen will lead to errors due to a carrier gas effect on pressure-broadening of the CO2 absorption lines since oxygen gas has a smaller line-broadening coefficient than nitrogen. FIGURE 9-5. ECMon zero-and-span window 9. Remove the CO2 span gas from the inlet of the shroud, and replace it with H2O span gas from a dew-point generator or another standard reference. Because water molecules can adsorb to inside of the tubing and the shroud, it may take many minutes for the H2O concentration to stabilize. If desired, increase the flow rate for the first several minutes to more quickly stabilize the system before returning it to between 0.4 and 0.6 l/min to make the H2O measurement. Write down the reported H2O concentration. 10. Remove the H2O span gas, and connect a zero air source (no CO2 or H2O) to the inlet tube of the shroud. As described in step 8, use a pressure regulator and flow controller so that zero air flows through the shroud between 0.4 and 0.6 l/min. Wait for the measurement readings to stabilize (this may require several minutes) and write down the reported values for CO2 and H2O concentrations. If the readings remain erratic, ensure that flow of the zero air is sufficient and the shroud is correctly seated on the snouts. 31