D-Link DGS-3048 Product Manual - Page 91
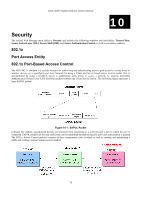
Authentication Server, Authenticator, Three Functions of 802.1x
 |
UPC - 790069287367
View all D-Link DGS-3048 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
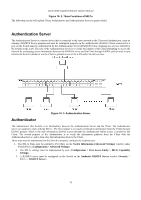
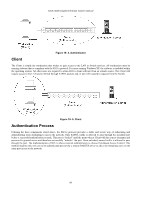
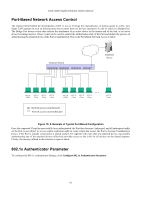
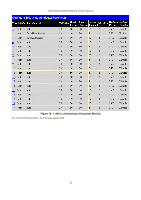
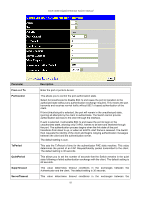
DGS-3048 Gigabit Ethernet Switch Manual Figure 10- 2. Three Functions of 802.1x The following section will explain Client, Authenticator, and Authentication Server in greater detail. Authentication Server The Authentication Server is a remote device that is connected to the same network as the Client and Authenticator, must be running a RADIUS Server program and must be configured properly on the Authenticator (Switch). Clients connected to a port on the Switch must be authenticated by the Authentication Server (RADIUS) before attaining any services offered by the Switch on the LAN. The role of the Authentication Server is to certify the identity of the Client attempting to access the network by exchanging secure information between the RADIUS server and the Client through EAPOL packets and, in turn, informs the Switch whether or not the Client is granted access to the LAN and/or Switch services. Figure 10- 3. Authentication Server Authenticator The Authenticator (the Switch) is an intermediary between the Authentication Server and the Client. The Authenticator serves two purposes when utilizing 802.1x. The first purpose is to request certification information from the Client through EAPOL packets, which is the only information allowed to pass through the Authenticator before access is granted to the Client. The second purpose of the Authenticator is to verify the information gathered from the Client with the Authentication Server, and to then relay that information back to the Client. Three steps must be implemented on the Switch to properly configure the Authenticator. I. The 802.1x State must be enabled to Port Base on the Switch Information (Advanced Settings) window under Switch 802.1x (Configuration > Advanced Settings). 4. The 802.1x settings must be implemented by port. (Configuration > Port Access Entity > 802.1x Capability Settings). 5. A RADIUS server must be configured on the Switch on the Authentic RADIUS Server window (Security > 802.1x > RADIUS Server). 79