Dell PowerVault TL4000 SCSI Reference Guide - Page 60
Parameter, Length, Field, descriptions, Reservation, Service, Action, Scope-Specific, Address, APTPL
 |
View all Dell PowerVault TL4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
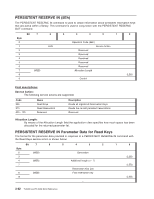
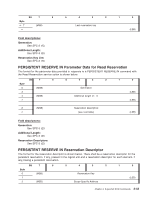
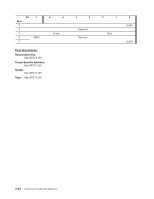
0h 1h 2h 3h - Fh Persistent reservation applies to the full logical unit Obsolete Persistent reservation applies to the specified element Reserved Parameter List Length: The Parameter List Length shall be set to the length of the Persistent Reserve Out Parameter List structure. PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT Parameter List The format for the reservation descriptor is shown below. There shall be a reservation descriptor for the persistent reservation, if any, present in the logical unit and a reservation descriptor for each element, if any, having a persistent reservation. Bit 7 6 Byte 0 (MSB) 7 8 (MSB) 15 16 (MSB) 19 20 21 22 (MSB) 23 5 4 3 2 Reservation Key Service Action Reservation Key Scope-Specific Address Reserved Reserved Obsolete 1 0 (LSB) (LSB) (LSB) APTPL (LSB) Field descriptions: Reservation Key: The Reservation Key field contains a value provided by the application client to the device server to identify the initiator that is the source of the PERSISTENT RESERVE OUT command. Service Action Reservation Key: For the Register, and Register and Ignore Existing Key service action, the Service Action Reservation Key contains the new registration key to be registered. For the Preempt, and Preempt and Abort service actions, the Service Action Reservation Key field contains the reservation key of the persistent reservations that are being preempted. The Service Action Reservation Key field is ignored for all other service actions. Scope-Specific Address: If the Scope is an Element Scope reservation, the Scope-Specific Address field shall contain the element address (zero filled in the most significant two bytes). APTPL: The Activate Persist Through power Loss (APTPL) bit shall be valid only for the Register, or the Register and Ignore Existing Key service action. In all other cases the APTPL bit shall be ignored. 3-46 TL2000 and TL4000 SCSI Reference