Dell S510n Dell Interactive Projector S510/ Users Guide - Page 151
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - A network protocol
 |
View all Dell S510n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
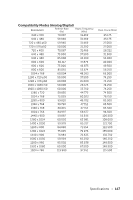
Page 151 highlights
average light output of the black rectangles to determine the ANSI contrast ratio. Full On/Off contrast is always a larger number than ANSI contrast for the same projector. dB - decibel - A unit used to express relative difference in power or intensity, usually between two acoustic or electric signals, equal to ten times the common logarithm of the ratio of the two levels. Diagonal Screen - A method of measuring the size of a screen or a projected image. It measures from one corner to the opposite corner. A 9 FT high, 12 FT wide, screen has a diagonal of 15 FT. This document assumes that the diagonal dimensions are for the traditional 4:3 ratio of a computer image as per the example above. DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - A network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign a TCP/IP address to a device. DLP® - Digital Light Processing™ - Reflective display technology developed by Texas Instruments, using small manipulated mirrors. Light passing through a color filter is sent to the DLP mirrors which arrange the RGB colors into a picture projected onto screen, also known as DMD. DMD - Digital Micro-Mirror Device - Each DMD consists of thousands of tilting, microscopic aluminum alloy mirrors mounted on a hidden yoke. DNS - Domain Name System - An Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. Focal Length - The distance from the surface of a lens to its focal point. Frequency - It is the rate of repetition in cycles per seconds of electrical signals. Measured in Hz (Hertz). HDCP - High-Bandwidth Digital-Content Protection - A specification developed by Intel™ Corporation to protect digital entertainment across digital interface, such as DVI, HDMI. HDMI - High-Definition Multimedia Interface - HDMI carries both uncompressed high definition video along with digital audio and device control data in a single connector. Hz (Hertz) - Unit of frequency. IEEE802.11 - A set of standards for wireless local are network (WLAN) communication. 802.11b/g/n uses the 2.4 GHz band. Keystone Correction - Device that will correct an image of the distortion (usually a wide-top narrow-bottom effect) of a projected image caused by improper projector to screen angle. Glossary 151