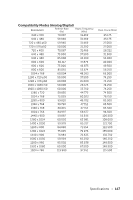
Dell S510n Dell Interactive Projector S510/ Users Guide - Page 152
Maximum Distance, Maximum Image Size, Reverse Image, SECAM
 |
View all Dell S510n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 152 highlights
Maximum Distance - The distance from a screen the projector can be to cast an image that is usable (bright enough) in a fully darkened room. Maximum Image Size - The largest image a projector can throw in a darkened room. This is usually limited by focal range of the optics. Minimum Distance - The closest position that a projector can focus an image onto a screen. NTSC - National Television Standards Committee. North American standard for video and broadcasting, with a video format of 525 lines at 30 frames per second. PAL - Phase Alternating Line. A European broadcast standard for video and broadcasting, with a video format of 625 lines at 25 frames per second. Reverse Image - Feature that allows you to flip the image horizontally. When used in a normal forward projection environment text, graphics, etc. are backwards. Reverse image is used for rear projection. RGB - Red, Green, Blue - typically used to describe a monitor that requires separate signals for each of the three colors. SECAM - A French and international broadcast standard for video and broadcasting, closely related to PAL but with a different method of sending color information. SSID - Service Set Identifiers - A name used to identify the particular wireless LAN to which a user wants to connect. SVGA - Super Video Graphics Array - 800 x 600 pixels count. SXGA - Super Extended Graphics Array, - 1280 x 1024 pixels count. UXGA - Ultra Extended Graphics Array - 1600 x 1200 pixels count. VGA - Video Graphics Array - 640 x 480 pixels count. WEP - Wired Equivalent Privacy - This is a method for encrypting communication data. The encryption key is created and notified only to the communicating user, so the communication data cannot be decrypted by a third party. XGA - Extended Video Graphics Array - 1024 x 768 pixels count. WXGA - Wide Extended Graphics Array - 1280 x 800 pixels count. 152 Glossary