Dell Z9100 EMC Networking with Isilon Front-End Deployment and Best Practices - Page 16
Layer 3 Topology preparation, 5.1 BGP ASN configuration, 5.2 Loopback addresses
 |
View all Dell Z9100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
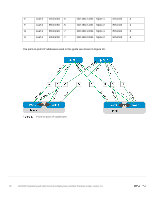
5 5.1 Layer 3 Topology preparation The layer 3 topology used in this example will use external border gateway protocol (eBGP) as well as ECMP. In order to correctly configure this topology, several things need to be considered and planned. BGP ASN configuration When eBGP is used, an autonomous system number (ASN) is assigned to each switch. Valid private, 2-byte ASNs range from 64512 through 65534. Figure 14 shows the ASN assignments used for leaf and spine switches in the BGP examples in this guide. 5.2 BGP ASN assignments ASNs should follow a logical pattern for ease of administration and allow for growth as additional leaf and spine switches are added. In this example, an ASN with a "6" in the hundreds place represents a spine switch (e.g., 64601), and an ASN with a "7" in the hundreds place represents a leaf switch (e.g., 64701). Note: The same ASN can be used across all tier-2 spine switches if the growth plans do not require an additional layer of spine switches. Loopback addresses Loopback addresses may be used as router IDs when configuring routing protocols. As with ASNs, loopback addresses should follow a logical pattern that will make it easier for administrators to manage the network and allow for growth. Figure 15 shows the loopback addresses used as router IDs in the example provided. 16 Dell EMC Networking with Isilon Front-End Deployment and Best Practices Guide | version 1.0