Edimax AR-7186WnB Manual - Page 71
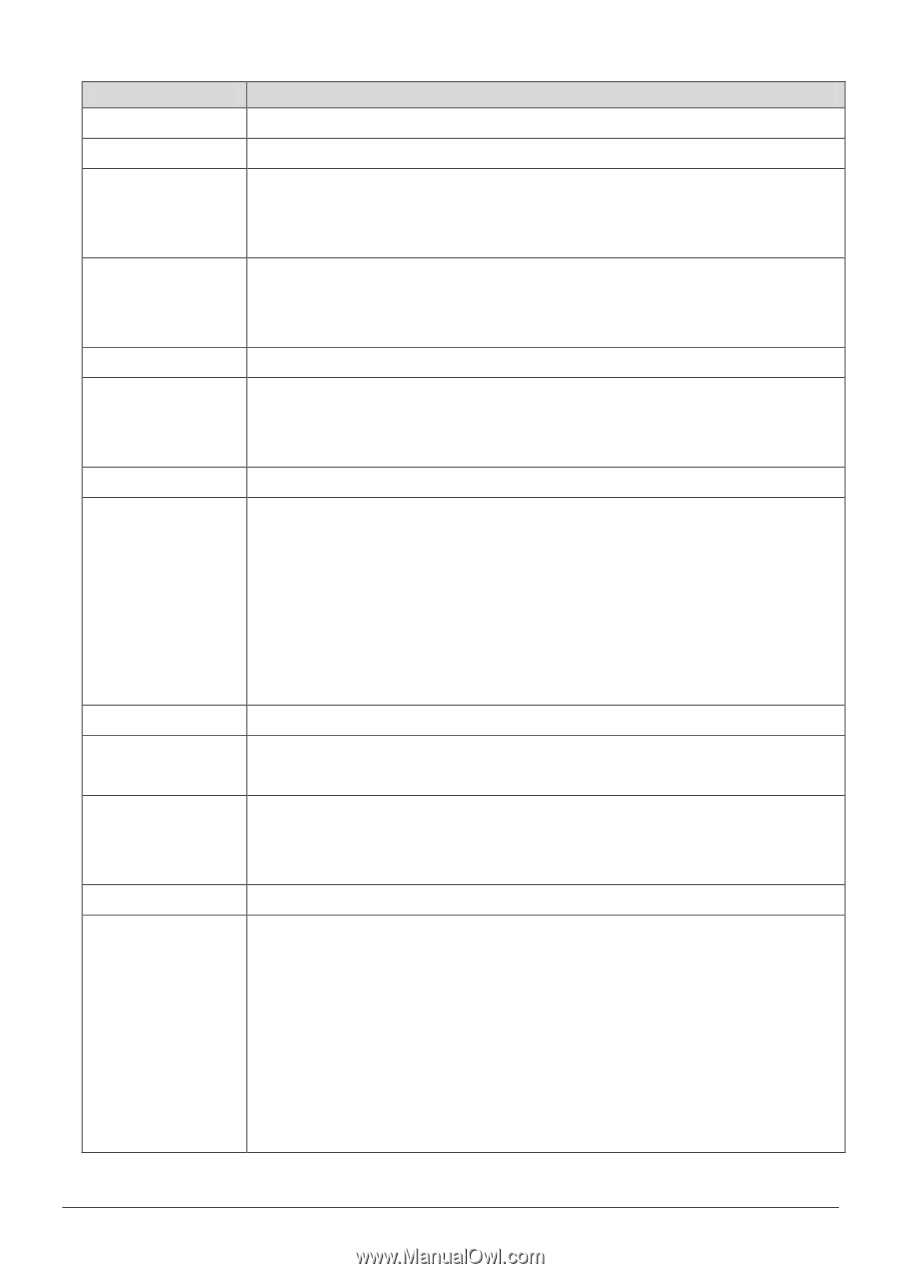
Field, Description, TCP/UDP, IPP/TOS, Normal service, Minimize, delay, Maximize throughput, Maximize
 |
View all Edimax AR-7186WnB manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 71 highlights
Field Description MGCP, SNMP, DNS, DHCP, RIP, RSTP, RTCP and RTP. Physical Ports Choose an Ethernet interface or WLAN Interface. Destination MAC The Destination MAC address of the rule. If data packets include the MAC address, the data packets are placed into the group. The destination IP address of the rule. If data packets IP include the IP address, the data packets are placed into the group. Port Range Port Range is from 0 to 65535. The Source MAC address of the rule. If data packets include Source MAC the MAC address, the data packets are placed into the group. Protocol ID You can choose TCP/UDP, TCP, UDP, ICMP or IGMP. Select this option to Activate/Deactivate the 4094 VID on the 4 different queues. VID (VLAN ID) is the identification of the VLAN, which is basically used by the standard Vlan ID Range 802.1Q. It has 12 bits and allows the identification of 4096 (2^12) VLANs. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is used to identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN configurations are 4,094. IPP/DS Field You may set IPP/TOS or DSCP. IP Precedence When IPP/DS field is set to IPP/TOS, you need to enter an Range IP precedence range. Support services including Normal service, Minimize Type of Service delay, Maximize throughput, Maximize reliability and Minimize monetary cost. DSCP Range DSCP Range is from 0 to 63. Select this option to Activate/Deactivate the 802.1p. IEEE 802.1p establishes eight levels of priority (0-7). Although network managers must determine actual mappings, IEEE 802.1p has made broad recommendations. Seven is the highest priority which is usually assigned to network-critical traffic such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) table updates. Five and six are often for delay-sensitive applications such as interactive 71