HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Gu - Page 138
Controlling SPF calculation interval, Configuring convergence priorities for specific routes
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 138 highlights
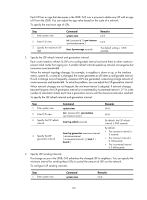
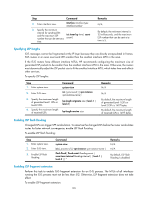
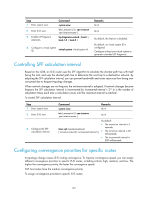
Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter IS-IS view. 3. Enable LSP fragment extension. Command system-view isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] lsp-fragments-extend [ level-1 | level-1-2 | level-2 ] 4. Configure a virtual system ID. virtual-system virtual-system-id Remarks N/A N/A By default, this feature is disabled. By default, no virtual system ID is configured. Configure at least one virtual system to generate extended LSP fragments. Controlling SPF calculation interval Based on the LSDB, an IS-IS router uses the SPF algorithm to calculate the shortest path tree with itself being the root, and uses the shortest path tree to determine the next hop to a destination network. By adjusting the SPF calculation interval, you can prevent bandwidth and router resources from being over consumed due to frequent topology changes. When network changes are not frequent, the minimum-interval is adopted. If network changes become frequent, the SPF calculation interval is incremented by incremental-interval × 2n-2 (n is the number of calculation times) each time a calculation occurs until the maximum-interval is reached. To control SPF calculation interval: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter IS-IS view. 3. Configure the SPF calculation interval. Command Remarks system-view N/A isis [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] N/A timer spf maximum-interval [ minimum-interval [ incremental-interval ] ] By default: • The maximum interval is 5 seconds. • The minimum interval is 50 milliseconds. • The incremental interval is 200 milliseconds. Configuring convergence priorities for specific routes A topology change causes IS-IS routing convergence. To improve convergence speed, you can assign different convergence priorities to specific IS-IS routes, including critical, high, medium, and low. The higher the convergence priority, the faster the convergence speed. IS-IS host routes have the medium convergence priority. To assign convergence priorities to specific IS-IS routes: 127