HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Gu - Page 65
DR and BDR election, Protocols and standards
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
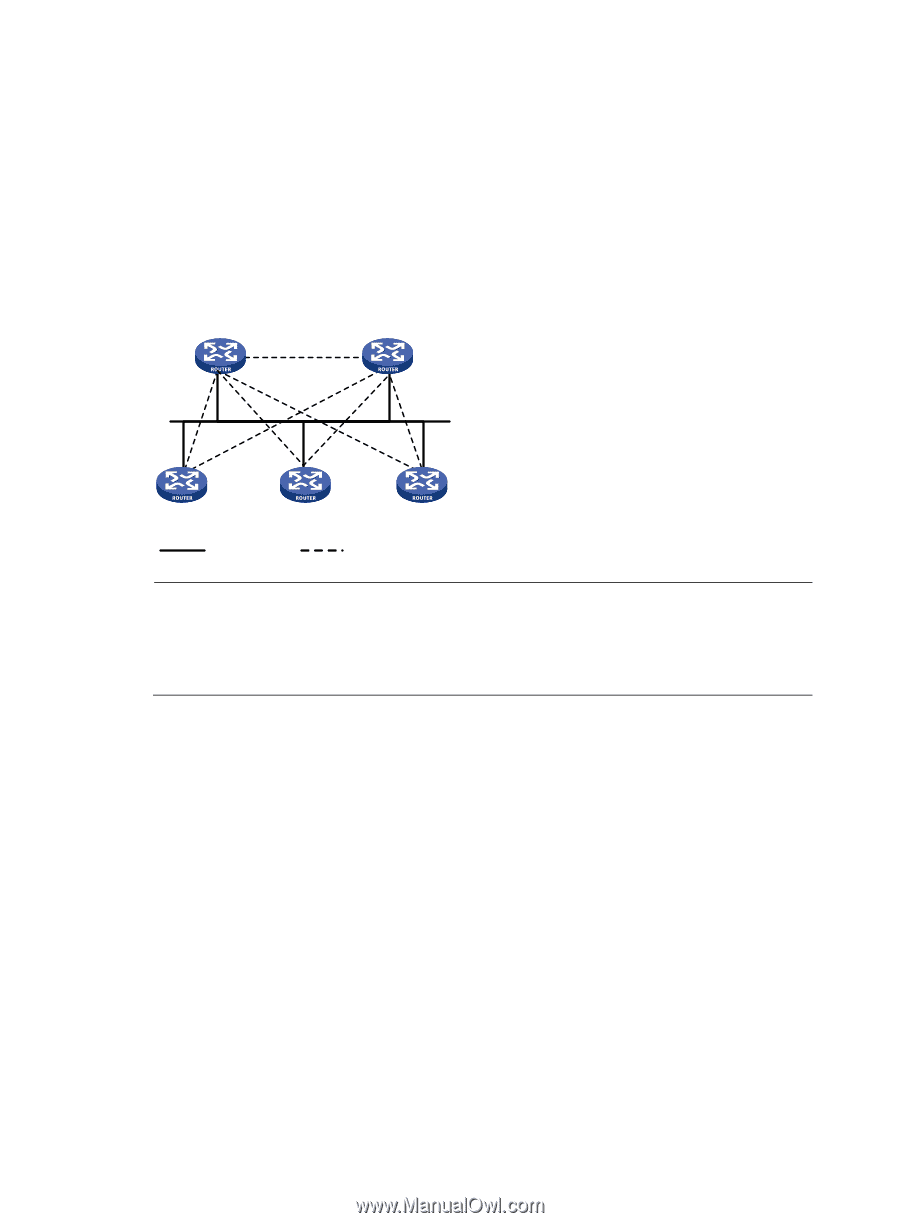
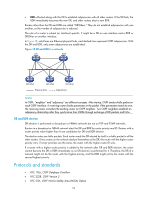
• BDR-Elected along with the DR to establish adjacencies with all other routers. If the DR fails, the BDR immediately becomes the new DR, and other routers elect a new BDR. Routers other than the DR and BDR are called "DROthers." They do not establish adjacencies with one another, so the number of adjacencies is reduced. The role of a router is subnet (or interface) specific. It might be a DR on one interface and a BDR or DROther on another interface. In Figure 18, solid lines are Ethernet physical links, and dashed lines represent OSPF adjacencies. With the DR and BDR, only seven adjacencies are established. Figure 18 DR and BDR in a network DR BDR DR other DR other DR other Physical links Adjacencies NOTE: In OSPF, "neighbor" and "adjacency" are different concepts. After startup, OSPF sends a hello packet on each OSPF interface. A receiving router checks parameters in the packet. If the parameters match its own, the receiving router considers the sending router an OSPF neighbor. Two OSPF neighbors establish an adjacency relationship after they synchronize their LSDBs through exchange of DD packets and LSAs. DR and BDR election DR election is performed on broadcast or NBMA networks but not on P2P and P2MP networks. Routers in a broadcast or NBMA network elect the DR and BDR by router priority and ID. Routers with a router priority value higher than 0 are candidates for DR and BDR election. The election votes are hello packets. Each router sends the DR elected by itself in a hello packet to all the other routers. If two routers on the network declare themselves as the DR, the router with the higher router priority wins. If router priorities are the same, the router with the higher router ID wins. If a router with a higher router priority is added to the network after DR and BDR election, the router cannot become the DR or BDR immediately as no DR election is performed for it. Therefore, the DR of a network might not be the router with the highest priority, and the BDR might not be the router with the second highest priority. Protocols and standards • RFC 1765, OSPF Database Overflow • RFC 2328, OSPF Version 2 • RFC 3101, OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) Option 54