HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Gu - Page 179
Address family, BGP configuration views
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 179 highlights
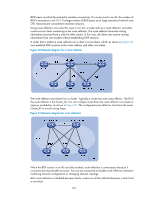
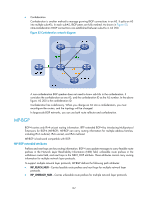
MP-BGP uses these two attributes to advertise feasible and unfeasible routes for different network layer protocols. BGP speakers not supporting MP-BGP ignore updates containing these attributes and do not forward them to its peers. The current MP-BGP implementation supports multiple protocol extensions, including VPN, IPv6, and multicast. For more information about VPN, see MCE Configuration Guide. Address family MP-BGP uses address families and subsequent address families to identify different network layer protocols for routes contained in the MP_REACH_NLRI and MP_UNREACH_NLRI attributes. For example, an Address Family Identifier (AFI) of 2 and a Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) of 1 identify IPv6 unicast routing information carried in the MP_REACH_NLRI attribute. For address family values, see RFC 1700. BGP configuration views BGP uses different views to manage routing information for different address families and different VPN instances. Most BGP commands are available in all BGP views. BGP supports multiple VPN instances by establishing a separate routing table for each VPN. Table 7 describes different BGP views. Table 7 BGP views View names BGP view BGP IPv4 unicast instance view BGP IPv6 unicast instance view BGP-VPN instance view Ways to enter the views system-view [Sysname] bgp 100 [Sysname-bgp] Remarks Configurations in this view are effective for routes of all address families on the public network and in all VPN instances (such as confederation, GR, and logging configurations), or only for routes of all address families on the public network. system-view [Sysname] bgp 100 [Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [Sysname-bgp-ipv4] Configurations in this view are effective for IPv4 unicast routes on the public network. system-view [Sysname] bgp 100 [Sysname-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [Sysname-bgp-ipv6] system-view [Sysname] bgp 100 [Sysname-bgp] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [Sysname-bgp-vpn1] Configurations in this view are effective for IPv6 unicast routes on the public network. Configurations in this view are effective for routes of all address families in the specified VPN instance. 168