HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Gu - Page 190
Specifying the source interface for TCP connections
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 190 highlights
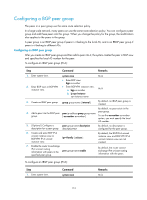
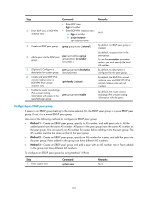
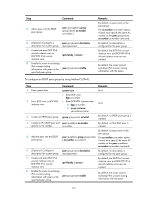
Step Command 6. Create and enter BGP IPv4 unicast instance view or BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast instance view. ipv4-family [ unicast ] 7. Enable the router to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peers in the peer group-name enable specified peer group. Remarks By default, the BGP IPv4 unicast instance view and BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast instance view are not created. By default, the router cannot exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with the peers. To configure an EBGP peer group by using Method 3 (IPv6): Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Enter BGP view or BGP-VPN instance view. • Enter BGP view: bgp as-number • Enter BGP-VPN instance view: a. bgp as-number b. ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name N/A 3. Create an EBGP peer group. group group-name external By default, no EBGP peer group is created. 4. Add a peer into the EBGP peer group. peer ipv6-address group By default, no peer exists in the group-name as-number as-number peer group. 5. (Optional.) Configure a peer group-name description description for the peer group. description-text By default, no description is configured for the peer group. 6. Create and enter BGP IPv6 unicast instance view or BGP-VPN IPv6 unicast instance view. ipv6-family [ unicast ] By default, the BGP IPv6 unicast instance view and BGP-VPN IPv6 unicast instance view are not created. 7. Enable the router to exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with peers in the peer group-name enable specified peer group. By default, the router cannot exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with the peers. Specifying the source interface for TCP connections By default, BGP uses the output interface of the optimal route to a peer or peer group as the source interface for establishing TCP connections to the peer or peer group, and it uses the IP address/IPv6 address of the output interface as the source IP address/IPv6 address of TCP connections. You can change the source interface in the following scenarios: • If the peer's IP address/IPv4 address belongs to an interface indirectly connected to the local router, you must specify that interface as the source interface for TCP connections on the peer. For example, interface A on the local end is directly connected to interface B on the peer. If you use the peer x.x.x.x as-number as-number command in which x.x.x.x is not the IP address of interface B on the local end, you must use the peer connect-interface command on the peer to specify the interface whose IP address is x.x.x.x as the source interface for establishing a TCP connection. 179