HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Gu - Page 175
Settlements for problems in large-scale BGP networks
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 175 highlights
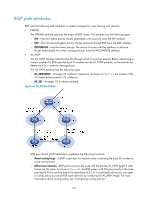
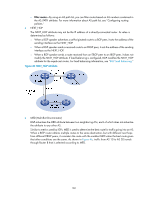
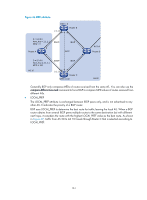
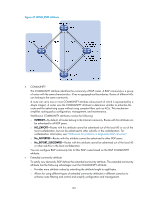
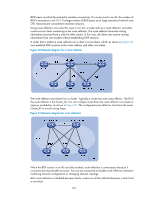
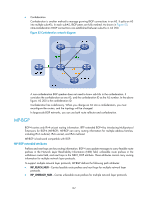
The system supports BGP load balancing based on route recursion. If multiple recursive routes to the same destination are load balanced (suppose three direct next hop addresses), BGP generates the same number of next hops to forward packets. BGP load balancing based on route recursion is always enabled by the system rather than configured by using commands. • BGP load balancing through route selection. BGP differs from IGP in the implementation of load balancing in the following ways: { IGP routing protocols, such as RIP and OSPF, compute metrics of routes, and then implement load balancing over routes with the same metric and to the same destination. The route selection criterion is metric. { BGP has no route computation algorithm, so it cannot implement load balancing according to metrics of routes. However, BGP has abundant route selection rules, through which, it selects available routes for load balancing and adds load balancing to route selection rules. BGP implements load balancing only on routes that have the same AS_PATH, ORIGIN, LOCAL_PREF and MED, rather than using the route selection rules as described in "BGP route selection." Figure 48 Network diagram In Figure 48, Router A and Router B are IBGP peers of Router C. Router D and Router E both advertise a route 9.0.0.0 to Router C. If load balancing with a maximum number of two routes is configured on Router C, and the two routes have the same AS_PATH, ORIGIN, LOCAL_PREF, and MED, Router C installs both the two routes to its routing table for load balancing. After that, Router C forwards to Router A and Router B a single route that has NEXT_HOP changed to Router C and other attributes changed to those of the best route. NOTE: BGP load balancing is applicable between EBGP peers, between IBGP peers, and between confederations. Settlements for problems in large-scale BGP networks You can use the following methods to facilitate management and improve route distribution efficiency on a large-scale BGP network. • Route summarization 164