HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch MCE Configuration Guide - Page 10
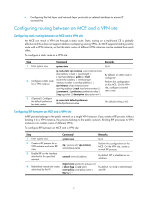
Configuring routing between an MCE and a VPN site
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
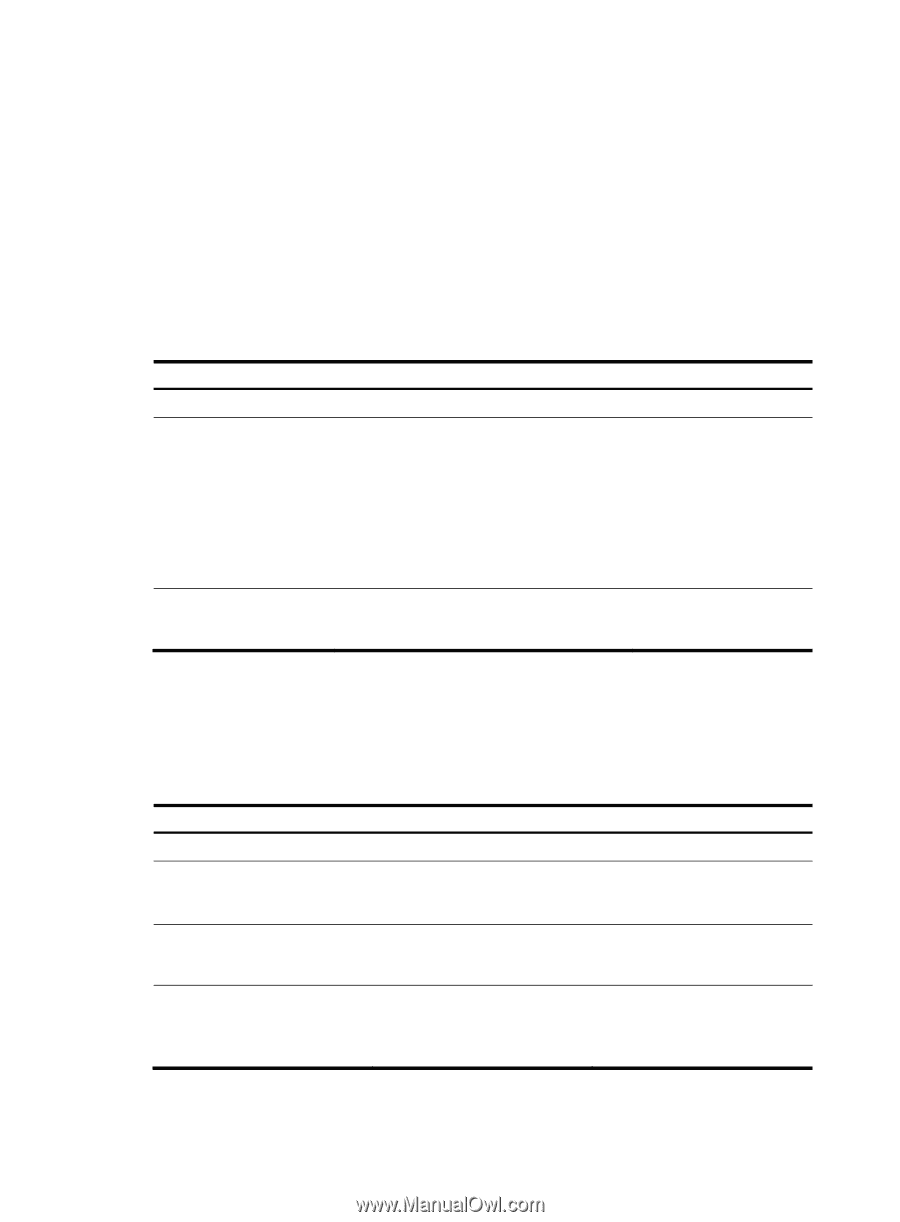
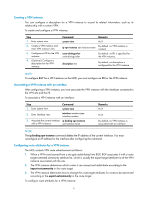
• Configuring the link layer and network layer protocols on related interfaces to ensure IP connectivity. Configuring routing between an MCE and a VPN site Configuring static routing between an MCE and a VPN site An MCE can reach a VPN site through a static route. Static routing on a traditional CE is globally effective and thus does not support address overlapping among VPNs. An MCE supports binding a static route with a VPN instance, so that the static routes of different VPN instances can be isolated from each other. To configure a static route to a VPN site: Step Command 1. Enter system view. system-view ip route-static vpn-instance s-vpn-instance-name dest-address { mask | mask-length } { next-hop-address [ public ] [ track 2. Configure a static route track-entry-number ] | interface-type for a VPN instance. interface-number [ next-hop-address ] | vpn-instance d-vpn-instance-name next-hop-address [ track track-entry-number ] } [ permanent ] [ preference preference-value ] [ tag tag-value ] [ description description-text ] 3. (Optional.) Configure the default preference for static routes. ip route-static default-preference default-preference-value Remarks N/A By default, no static route is configured. Perform this configuration on the MCE. On the VPN site, configure a normal static route. The default setting is 60. Configuring RIP between an MCE and a VPN site A RIP process belongs to the public network or a single VPN instance. If you create a RIP process without binding it to a VPN instance, the process belongs to the public network. Binding RIP processes to VPN instances can isolate routes of different VPNs. To configure RIP between an MCE and a VPN site: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 2. Create a RIP process for a VPN instance and enter RIP view. 3. Enable RIP on the interface attached to the specified network. rip [ process-id ] vpn-instance vpn-instance-name network network-address Perform this configuration on the MCE. On the VPN site, create a normal RIP process. By default, RIP is disabled on an interface. import-route protocol [ process-id ] 4. Redistribute remote site routes [ allow-ibgp ] [ cost cost | By default, no route is redistributed advertised by the PE. route-policy route-policy-name | into RIP. tag tag ] * 7