HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch MCE Configuration Guide - Page 17
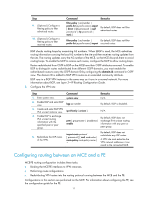
Configuring IS-IS between an MCE and a PE, Configuring EBGP between an MCE and a PE
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
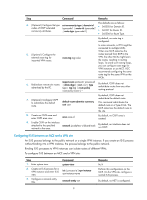
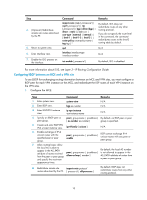
Configuring IS-IS between an MCE and a PE Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Create an IS-IS process for a VPN instance and isis [ process-id ] vpn-instance enter IS-IS view. vpn-instance-name N/A 3. Configure a network entity title. network-entity net By default, no NET is configured. import-route { isis [ process-id ] | ospf By default, IS-IS does not [ process-id ] | rip [ process-id ] | bgp redistribute routes of any other 4. (Optional.) Redistribute [ allow-ibgp ] | direct | static } [ cost cost routing protocol. the VPN routes. | cost-type { external | internal } | If you do not specify the route level [ level-1 | level-1-2 | level-2 ] | in the command, the command route-policy route-policy-name | tag redistributes routes to the level-2 tag ] * routing table by default. 5. (Optional.) Configure a filter-policy { acl-number | prefix-list filtering policy to filter prefix-list-name | route-policy the redistributed routes. route-policy-name } import By default, IS-IS does not filter redistributed routes. 6. Return to system view. quit N/A 7. Enter interface view. interface interface-type interface-number N/A 8. Enable the IS-IS process on the interface. isis enable [ process-id ] By default, no IS-IS process is enabled. For more information about IS-IS, see Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide. Configuring EBGP between an MCE and a PE Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. 2. Enable BGP and enter BGP view. system-view bgp as-number N/A By default, BGP is not enabled. 3. Enter BGP-VPN instance view. ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name N/A 4. Specify the PE as the EBGP peer. peer { group-name | ip-address } [ as-number as-number ] 5. Create and enter BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast instance view. ipv4-family [ unicast ] 6. Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information peer { group-name | ip-address } with the specified peer or enable peer group. By default, no BGP peer or peer group is specified. N/A By default, BGP does not exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with any peer or peer group. 7. Redistribute the VPN routes of import-route protocol [ process-id the VPN site. | all-processes ] By default, BGP does not redistribute routes from any other routing protocol. 8. (Optional.) Configure a filtering policy to filter the routes to be advertised. filter-policy { acl-number | prefix-list ip-prefix-name } export [ direct | isis process-id | ospf process-id | rip process-id | static ] By default, BGP does not filter the routes to be advertised. 14