HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch MCE Configuration Guide - Page 24
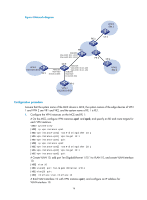
Using BGP to advertise VPN routes to the PE, Network requirements
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
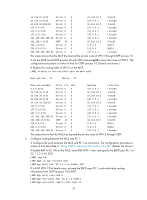
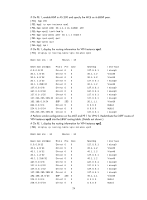
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn2 Destinations : 13 Routes : 13 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface 0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 40.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 40.1.1.2 Vlan40 40.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 40.1.1.2 Vlan40 40.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 40.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 40.1.1.2 Vlan40 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 192.168.10.0/24 OSPF 150 1 40.1.1.1 Vlan40 224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0 224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 The output shows that PE 1 has learned the private route of VPN 2 through OSPF. Now, the routing information for the two VPNs has been redistributed into the VPN routing tables on PE 1. Using BGP to advertise VPN routes to the PE Network requirements As shown in Figure 5, configure the MCE to advertise the routes of VPNs 1 and 2 to PE 1, so that the sites of each VPN can communicate with each other over the MPLS backbone. Run OSPF in both VPNs 1 and 2, and run EBGP between the MCE and PE 1. 21