HP EliteBook Folio 1000 HP EliteBook Folio 1040 G1 Notebook PC Maintenance and - Page 112
Questions and answers
 |
View all HP EliteBook Folio 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
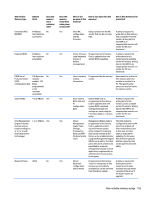
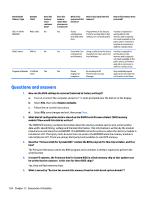
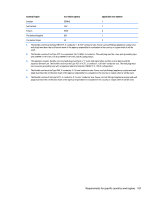
Non Volatile Memory Type Amount (Size) 802.11 WLAN EEPROM 4kb to 8kb Web Camera 64K bit Fingerprint Reader 512kByte Flash Does this memory store customer data? No No Yes Does this memory retain data when power is removed? What is the purpose of this memory? How is data input into this memory? How is this memory write protected? Yes Stores Programmed at the factory. A utility is required for configuration Tools for writing data to this writing data to this and calibration memory are not made public. memory and is typically data. not made available to the public unless a firmware upgrade is necessary to address a unique issue. Yes Store Web Cam Using a utility from the device A utility is required for configuration manufacturer that can be run writing data to this and firmware. from Windows. memory and is typically not made available to the public unless a firmware upgrade is necessary to address a unique issue. Yes Stores By enrolling in HP Only a digitally signed fingerprint ProtectTools Security application can make the templates. Manager. call to write to the flash. Questions and answers 1. How can the BIOS settings be restored (returned to factory settings)? a. Turn on or restart the computer and press F10 when prompted near the bottom of the display. b. Select File, then select Restore defaults. c. Follow the on-screen instructions. d. Select File, save changes and exit, then press Enter. 2. What kind of configuration data is stored on the DIMM Serial Presence Detect (SPD) memory module? How would this data be written? The DIMM SPD memory contains information about the memory module such as size, serial number, data width, speed/timing, voltage and thermal information. This information is written by the module manufacturer and stored on an EEPROM. This EEPROM cannot be written to when the memory module is installed in a PC. Third party tools do exist that can write to the EEPROM when the memory module is not installed in a PC. There are various third party tools available to read SPD memory. 3. Does the "Firmware Hub for System BIOS" contain the BIOS program? Is this chip writable, and if so how? The Firmware Hub does contain the BIOS program and is writable. A utility is required to perform the write function. 4. In some PC systems, the Firmware Hub for System BIOS is a flash memory chip so that updates can be written by the customer. Is this true for these BIOS chips? Yes, they are flash memory chips. 5. What is meant by "Restore the nonvolatile memory found in Intel-based system boards"? 104 Chapter 13 Statement of Volatility