HP LH4r HP Netserver LC 3 NetRAID Installation Guide - Page 66
Setup RAID 1 and 10 Arrays
 |
View all HP LH4r manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 66 highlights
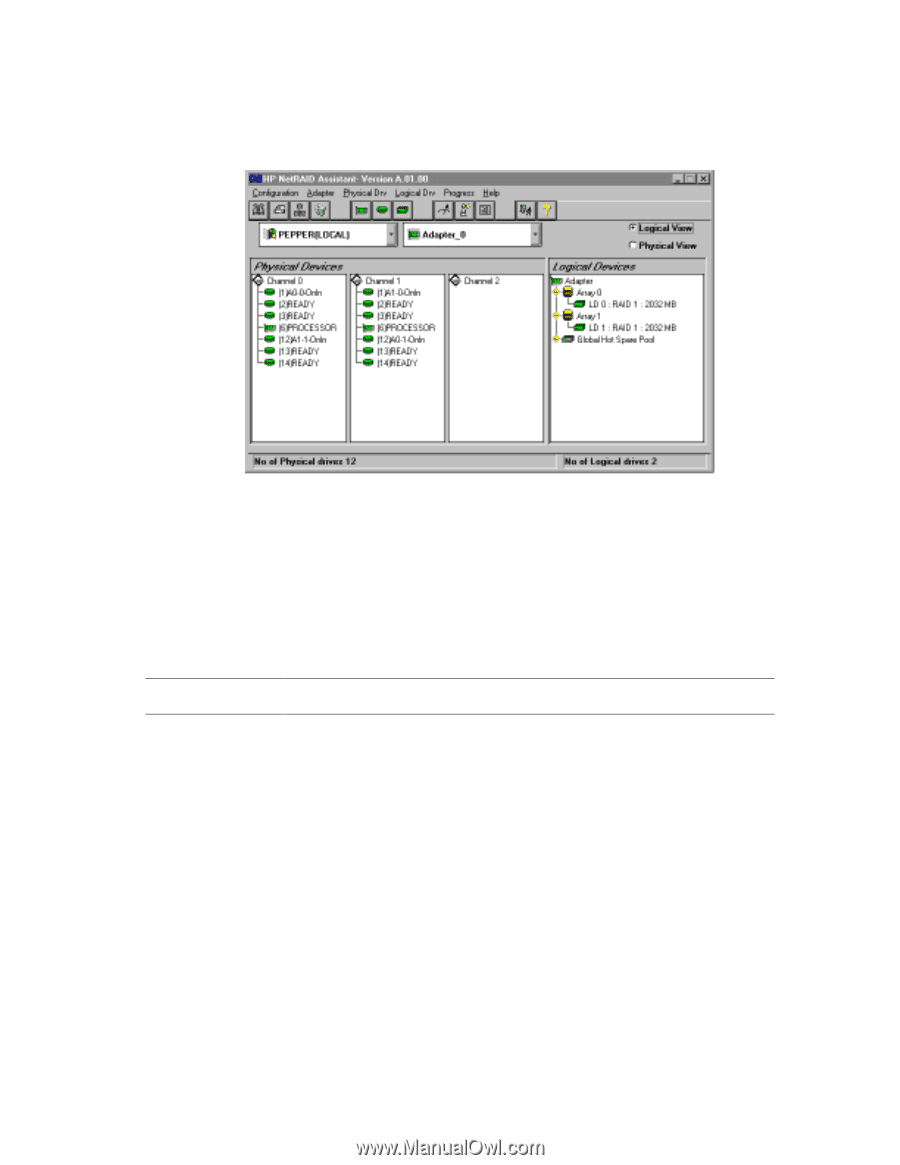
From the Windows NT Start menu, click Programs|NetRAID|NetRAID Assistant. The HP NetRAID Assistant program loads and displays its main window. HP NetRAID Assistant Screen HP NetRAID Assistant lists the Physical Devices (actual physical drives) and Logical Devices (RAID arrays) on the NetRAID Assistant screen. The Physical Devices heading lists the drives in columns by channel. Some clusters do not use channel 2 and so no devices will be listed. Likewise, some clusters only use one channel and so both channels 1 and 2 will be devoid of entries. To view the properties of a physical or logical device listed, double-click the device. The number in parentheses to the right of each physical drive icon is its SCSI ID. The state of each physical drive appears to the right of the SCSI ID. Initially the device will be described as READY. The possible states of a physical drive are as follows: The state... Onln Rdy or READY HOTSP FAILED REBUILDING Indicates the drive is... Online, functioning normally, and part of a configured array. Functioning normally, but not part of a configured logical drive nor configured as a hot spare. Configured as a hot spare, powered up and ready for use. Out of service because a fault occurred. Rebuilding an array on a new drive. Refer to the HP NetRAID User Guide in Information Assistant for more information about HP NetRAID Assistant. Setup RAID 1 and 10 Arrays Each RAID 1 disk array is composed of two hard (hot swap) drives located in external shared storage cabinets. RAID level 1 (mirroring) provides storage redundancy with maximum performance. A RAID 1 array consists of two drives that contain exactly the same data. That is, all of the data on one drive is replicated (mirrored) on the other. Since each drive contains a complete copy of all data, all data is still NetRAID Supplement to the HP NetServer Microsoft Cluster Installation Guide 19